Metro PCS 2009 Annual Report Download - page 127
Download and view the complete annual report
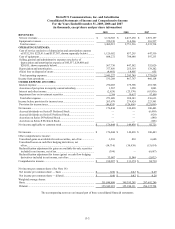
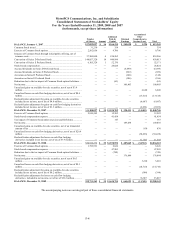
Please find page 127 of the 2009 Metro PCS annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.MetroPCS Communications, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007
F-13
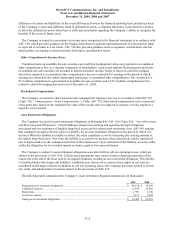
Earnings per Share
Basic earnings per share (“EPS”) are based upon the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for
the period. Diluted EPS is computed in the same manner as EPS after assuming issuance of common stock for all
potentially dilutive equivalent shares, whether exercisable or not.
In accordance with ASC 260 (Topic 260, “Earnings Per Share”), unvested share-based payment awards that
contain rights to receive non-forfeitable dividends or dividend equivalents, whether paid or unpaid, are considered a
“participating security” for purposes of computing earnings or loss per common share and the two-class method of
computing earnings per share is required for all periods presented. During the year ended December 31, 2009, the
Company issued restricted stock awards. Unvested shares of restricted stock are participating securities such that
they have rights to receive forfeitable dividends. In accordance with ASC 260, the unvested restricted stock was
considered a “participating security” for purposes of computing earnings per common share and was therefore
included in the computation of basic and diluted earnings per common share.
The Series D Preferred Stock and Series E Preferred Stock (collectively, the “preferred stock”) that was
outstanding during the year ended December 31, 2007 were participating securities, such that in the event a dividend
was declared or paid on the common stock, the Company would have simultaneously declared and paid a dividend
on the preferred stock as if they had been converted into common stock. In accordance with ASC 260, the preferred
stock was considered a “participating security” for purposes of computing earnings per common share and,
therefore, the preferred stock was included in the computation of basic and diluted earnings per common share using
the two-class method, except during periods of net losses. When determining basic earnings per common share
under ASC 260, undistributed earnings for a period were allocated to a participating security based on the
contractual participation rights of the security to share in those earnings as if all of the earnings for the period had
been distributed (See Note 16).
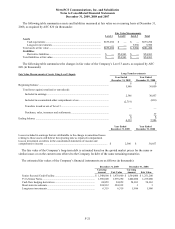
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In March 2008, the FASB issued SFAS No. 161, “Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging
Activities, an amendment of FASB Statement No. 133,” (“SFAS No. 161”) amending ASC 815 (Topic 815,
“Derivatives and Hedging”). SFAS No. 161 requires enhanced disclosures about a company’s derivative and
hedging activities. These enhanced disclosures discuss (a) how and why a company uses derivative instruments, (b)
how derivative instruments and related hedge items are accounted for under SFAS No. 133 and its related
interpretations, and (c) how derivative instruments and related hedged items affect a company’s financial position,
results of operations and cash flows. SFAS No. 161 became effective for fiscal years beginning on or after
November 15, 2008. The implementation of this standard did result in enhanced disclosures, but did not affect the
Company’s financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
In June 2009, the FASB issued SFAS No. 168, “The FASB Accounting Standards Codification and the Hierarchy
of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles – A Replacement of FASB No. 162,” (“SFAS No. 168”) amending
(ASC 105 (Topic 105, “Generally Accepted Accounting Principles”)). SFAS 168 replaces SFAS No. 162, “The
Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles,” and establishes the FASB Accounting Standards
CodificationTM, as the source of authoritative accounting principles recognized by the FASB to be applied by
nongovernmental entities in the preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP. SFAS No. 168 was
effective for interim or annual financial reporting periods ending after September 15, 2009. The implementation of
this standard did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations or cash
flows, but did change the way authoritative accounting pronouncements are referenced in the consolidated financial
statements.
In August 2009, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update 2009-05 (“ASU 2009-05”), “Measuring
Liabilities at Fair Value,” which updates ASC 820 (Topic 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures”).
ASU 2009-05 addresses the impact of transfer restrictions on the fair value of a liability that is traded as an asset as
an input to the valuation of the underlying liability, and clarifies when to make adjustments to fair value. ASU
2009-05 was effective for periods ending after August 26, 2009. The implementation of this standard did not have a
material impact on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.