Kraft 2006 Annual Report Download - page 97
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 97 of the 2006 Kraft annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
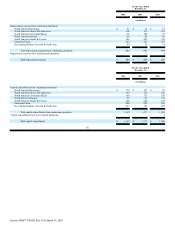
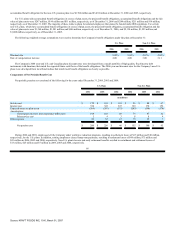
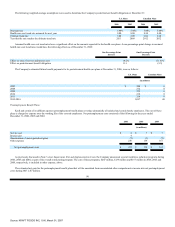
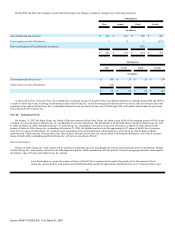
Minimum rental commitments under non-cancelable operating leases in effect at December 31, 2006, were as follows (in millions):
2007 $ 244
2008 202
2009 147
2010 107
2011 90
Thereafter 140
$ 930
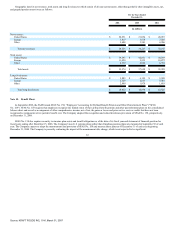
Note 17. Financial Instruments:
Derivative financial instruments:
The Company operates globally, with manufacturing and sales facilities in various locations around the world, and utilizes certain financial instruments to
manage its foreign currency and commodity exposures. Derivative financial instruments are used by the Company, principally to reduce exposures to market
risks resulting from fluctuations in foreign exchange rates and commodity prices by creating offsetting exposures. The Company is not a party to leveraged
derivatives and, by policy, does not use financial instruments for speculative purposes. Financial instruments qualifying for hedge accounting must maintain a
specified level of effectiveness between the hedging instrument and the item being hedged, both at inception and throughout the hedged period. The Company
formally documents the nature of and relationships between the hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as its risk-management objectives, strategies for
undertaking the various hedge transactions and method of assessing hedge effectiveness. Additionally, for hedges of forecasted transactions, the significant
characteristics and expected terms of the forecasted transaction must be specifically identified, and it must be probable that each forecasted transaction will
occur. If it were deemed probable that the forecasted transaction will not occur, the gain or loss would be recognized in earnings currently.
The Company uses forward foreign exchange contracts and foreign currency options to mitigate its exposure to changes in exchange rates from third-party
and intercompany actual and forecasted transactions. Substantially all of the Company's derivative financial instruments are effective as hedges. The primary
currencies to which the Company is exposed, based on the size and location of its businesses, include the euro, Swiss franc, British pound and Canadian dollar.
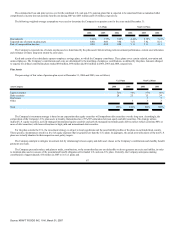
At December 31, 2006 and 2005, the Company had foreign exchange option and forward contracts with aggregate notional amounts of $2.6 billion and
$2.2 billion, respectively. The effective portion of unrealized gains and losses associated with forward and option contracts is deferred as a component of
accumulated other comprehensive earnings (losses) until the underlying hedged transactions are reported on the Company's consolidated statement of earnings.
The Company is exposed to price risk related to forecasted purchases of certain commodities used as raw materials by its businesses. Accordingly, the
Company uses commodity forward contracts as cash flow hedges, primarily for coffee, milk, sugar and cocoa. In general, commodity forward contracts qualify
for the normal purchase exception under SFAS No. 133 and are, therefore, not subject to the provisions of SFAS No. 133. In addition, commodity futures and
options are also used to hedge the price of certain commodities, including milk, coffee, cocoa, wheat, corn, sugar, soybean oil, natural gas and heating oil. For
qualifying contracts, the effective portion of unrealized gains and losses on commodity futures and option contracts is deferred as a component of accumulated
other comprehensive earnings (losses) and is recognized as a component of cost of sales in the Company's consolidated statement of earnings when the related
inventory is sold. Unrealized gains or losses on net commodity positions were
92
Source: KRAFT FOODS INC, 10-K, March 01, 2007