CarMax 2011 Annual Report Download - page 63
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 63 of the 2011 CarMax annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
53
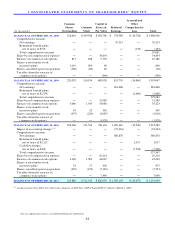
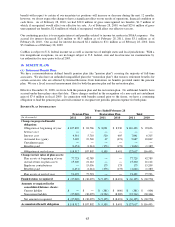
ENDING MANAGED RECEIVABLES BY MAJOR CREDIT GRADE
(In millions)
% (2)
A 2,234.1$ 51.5
B 1,668.0 38.5
C and other 432.5 10.0
Total ending managed receivables 4,334.6$ 100.0
As of February 28
2011 (1)
(1) Classified based on credit grade assigned when customers were approved for financing.
(2) Percent of total ending managed receivables.
5. SECURITIZATIONS
Securitization Financing. We maintain a revolving securitization program comprised of two warehouse facilities
(“warehouse facilities”) that we use to fund auto loan receivables originated by CAF until they are funded through a
term securitization or alternative funding arrangement. We sell the auto loan receivables to a wholly owned,
bankruptcy-remote, special purpose entity that transfers an undivided percentage ownership interest in the
receivables, but not the receivables themselves, to entities formed by third-party investors (“bank conduits”). The
bank conduits issue asset-backed commercial paper supported by the transferred receivables, and the proceeds from
the sale of the commercial paper are used to finance the securitized receivables.
The bank conduits may be considered variable interest entities, but are not consolidated because our interest does
not constitute a variable interest in the entities. We hold a variable interest in specified assets transferred to the
entities rather than interests in the entities themselves.
We typically use term securitizations to refinance the auto loan receivables previously securitized through the
warehouse facilities. The purpose of term securitizations is to provide long-term funding for these receivables. In
these transactions, a pool of auto loan receivables is sold to a bankruptcy-remote, special purpose entity that, in turn,
transfers the receivables to a special purpose securitization trust. The securitization trust issues asset-backed
securities, secured or otherwise supported by the transferred receivables, and the proceeds from the sale of the asset-
backed securities are used to finance the securitized receivables. Refinancing receivables in a term securitization
could have an impact on our results of operations depending on the transaction structure and market conditions.
The warehouse facilities and the term securitizations are governed by various legal documents that limit and specify
the activities of the special purpose entities and term securitization trusts (collectively, “securitization vehicles”)
used to facilitate the securitizations. The securitization vehicles are generally allowed to acquire the receivables
being sold to them, issue asset-backed securities to investors to fund the acquisition of the receivables and enter into
derivatives or other yield maintenance contracts to hedge or mitigate certain risks related to the pool of receivables
or asset-backed securities. Additionally, the securitization vehicles are required to service the receivables they hold
and the securities they have issued. These servicing functions are performed by CarMax, as appointed within the
underlying legal documents. Servicing functions include, but are not limited to, collecting payments from
borrowers, monitoring delinquencies, liquidating assets, investing funds until distribution, remitting payments to the
trustee who in turn remits payments to the investors, and accounting for and reporting information to investors.
The securitized receivables can only be used as collateral to settle obligations of the securitization vehicles. The
securitization vehicles and investors have no recourse to our assets beyond the securitized receivables, the amounts
on deposit in reserve accounts and the restricted cash from collections on auto loan receivables. We have not
provided financial or other support to the securitization vehicles or investors that was not previously contractually
required. There are no additional arrangements, guarantees or other commitments that could require us to provide
financial support to the securitization vehicles.
Financial Covenants and Performance Triggers. The securitization agreements related to the warehouse facilities
include various financial covenants and performance triggers. The financial covenants include a maximum total
liabilities to tangible net worth ratio and a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio. Performance triggers require that
the pools of securitized receivables in the warehouse facilities achieve specified thresholds related to loss and
delinquency rates. If these financial covenants and/or thresholds are not met, we could be unable to continue to
securitize receivables through the warehouse facilities. In addition, the warehouse facility investors would charge us
a higher rate of interest and could have us replaced as servicer. Further, we could be required to deposit collections
on the securitized receivables with the warehouse facility agents on a daily basis and deliver executed lockbox