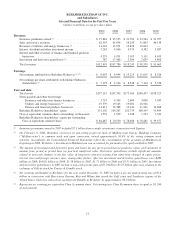
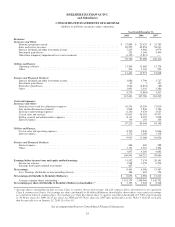
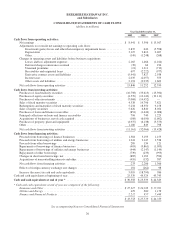
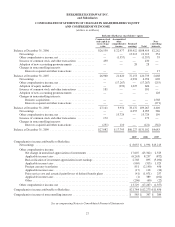
Berkshire Hathaway 2009 Annual Report Download - page 30
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 30 of the 2009 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY INC.
and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2009
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices
(a) Nature of operations and basis of consolidation
Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (“Berkshire”) is a holding company owning subsidiaries engaged in a number of diverse
business activities, including property and casualty insurance and reinsurance, utilities and energy, finance,
manufacturing, service and retailing. In these notes the terms “us,” “we,” or “our” refer to Berkshire and its
consolidated subsidiaries. Further information regarding our reportable business segments is contained in Note 22.
Significant business acquisitions completed over the past three years are discussed in Note 2.
The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of Berkshire consolidated with the
accounts of all subsidiaries and affiliates in which we hold a controlling financial interest as of the financial statement
date. Normally a controlling financial interest reflects ownership of a majority of the voting interests. Other factors
considered in determining whether a controlling financial interest is held include whether we possess the authority to
purchase or sell assets or make other operating decisions that significantly affect the entity’s results of operations and
whether we bear a majority of the financial risk of the entity. Intercompany accounts and transactions have been
eliminated. Certain amounts in prior year presentations have been reclassified to conform with the current year
presentation.
In 2009, the Financial Accounting Standards Board established the FASB Accounting Standards Codification ™ (the
“Codification”) as the source of accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”)
through the integration of then current accounting standards from several sources into a single source. The
Codification did not affect the content or application of GAAP that was in effect and had no material impact on our
Consolidated Financial Statements. In these notes, relevant accounting principles are identified by Accounting
Standards Codification number or “ASC.”
As of January 1, 2009, we adopted certain provisions of ASC 810 Consolidation which require that noncontrolling
interests (formerly known as “minority interests”) be displayed in the balance sheet as a separate component of
shareholders’ equity and that net earnings attributable to the noncontrolling interests be indentified and presented in
the statement of earnings. In addition, changes in ownership interests where the parent retains a controlling interest are
to be reported as transactions affecting shareholders’ equity. Previously such transactions were reportable as
additional investment purchases (potentially resulting in recognition of additional other assets, including goodwill, or
liabilities) or sales (potentially resulting in gains or losses). During 2009, we acquired certain noncontrolling interests
in subsidiaries that resulted in a reduction to shareholders’ equity attributable to Berkshire of approximately $121
million. The reduction represents the excess of consideration paid over the previously recorded balance sheet carrying
amount of the acquired noncontrolling (minority) interests.
(b) Use of estimates in preparation of financial statements
The preparation of our Consolidated Financial Statements in conformity with GAAP requires us to make estimates
and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the
reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the period. In particular, estimates of unpaid losses and loss
adjustment expenses and related recoverables under reinsurance for property and casualty insurance are subject to
considerable estimation error due to the inherent uncertainty in projecting ultimate claim amounts that will be settled
over many years. In addition, estimates and assumptions associated with the amortization of deferred charges
reinsurance assumed, determination of fair value of certain financial instruments and evaluation of goodwill for
impairment requires considerable judgment. Actual results may differ from the estimates used in preparing our
Consolidated Financial Statements.
(c) Cash and cash equivalents
Cash equivalents consist of funds invested in U.S. Treasury Bills, money market accounts, demand deposits and other
investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased.
28