Aflac 2008 Annual Report Download - page 86
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 86 of the 2008 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
82 Aflac Incorporated Annual Report for 2008
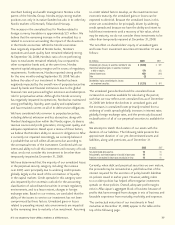
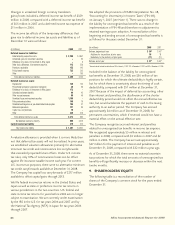
(In millions) 2008 2007 2006
Balance, beginning of period $ (47) $ (17) $ (22)
Increase (decrease) in fair value of cross-currency swaps (122) (26) 5
Interest rate component not qualifying for hedge accounting
reclassified to net earnings 5 (4) –
Balance, end of period $ (164) $ (47) $ (17)
The change in fair value of the interest-rate swaps, included
in accumulated other comprehensive income, was immaterial
during each of the years in the three-year period ended
December 31, 2008.
We are exposed to credit risk in the event of nonperformance
by counterparties to our cross-currency and interest-rate
swaps. The counterparties to our swap agreements are U.S.
and Japanese financial institutions with the following credit
ratings as of December 31.
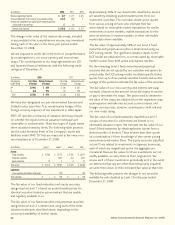
(In millions) 2008 2007
Counterparty Fair Value Notional Amount Fair Value Notional Amount
Credit Rating of Swaps of Swaps of Swaps of Swaps
AA $ (104) $ 300 $ (24) $ 387
A (54) 370 (11) 238
Total $ (158) $ 670 $ (35) $ 625
We have also designated our yen-denominated Samurai and
Uridashi notes (see Note 7) as nonderivative hedges of the
foreign currency exposure of our investment in Aflac Japan.
SFAS 157 specifies a hierarchy of valuation techniques based
on whether the inputs to those valuation techniques are
observable or unobservable. These two types of inputs create
three valuation hierarchy levels. The following table presents
the fair-value hierarchy levels of the Company’s assets and
liabilities under SFAS 157 that are measured at fair value on a
recurring basis as of December 31, 2008.
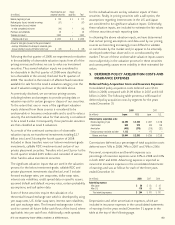
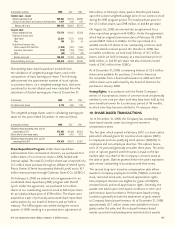
(In millions) Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Total
Assets:
Fixed maturities $ 10,298 $ 22,124 $ 2,590 $ 35,012
Perpetual securities – 7,635 412 8,047
Equity securities 18 5 4 27
Total assets $ 10,316 $ 29,764 $ 3,006 $ 43,086
Liabilities:
Cross-currency and interest-rate swaps – 158 – 158
Total liabilities $ – $ 158 $ – $ 158
The fair value of our fixed maturities and equity securities
categorized as Level 1 is based on quoted market prices for
identical securities traded in active markets that are readily
and regularly available to us.
The fair value of our fixed maturities and perpetual securities
categorized as Level 2 is determined using each of the three
valuation techniques described above, depending on the
source and availability of market inputs.
Approximately 36% of our investments classified as Level 2
are valued by obtaining quoted market prices from our
investment custodian. The custodian obtains price quotes
from various pricing services who estimate their fair
values based on observable market transactions for similar
investments in active markets, market transactions for the
same investments in inactive markets or other observable
market data where available.
The fair value of approximately 59% of our Level 2 fixed
maturities and perpetual securities is determined using our
DCF pricing model. The significant valuation inputs to the
DCF model are obtained from, or corroborated by, observable
market sources from both active and inactive markets.
For the remaining Level 2 fixed maturities and perpetual
securities that are not quoted by our custodian and cannot be
priced under the DCF pricing model, we obtain specific broker
quotes from up to three outside securities brokers and use the
average of the quotes to estimate the fair value of the securities.
The fair value of our cross-currency and interest-rate swap
contracts is based on the amount we would expect to receive
or pay to terminate the swaps. The prices used to determine
the value of the swaps are obtained from the respective swap
counterparties and take into account current interest and
foreign currency rates, duration, counterparty credit risk and
our own credit rating.
The fair value of our fixed maturities classified as Level 3
consists of securities for which there are limited or no
observable valuation inputs. We estimate the fair value of our
Level 3 fixed maturities by obtaining broker quotes from a
limited number of brokers. These brokers base their quotes
on a combination of their knowledge of the current pricing
environment and market flows. The equity securities classified
in Level 3 are related to investments in Japanese businesses,
each of which are insignificant and in the aggregate are
immaterial. Because fair values for these investments are not
readily available, we carry them at their original cost. We
review each of these investments periodically and, in the event
we determine that any are other-than-temporarily impaired,
we write them down to their estimated fair value at that time.
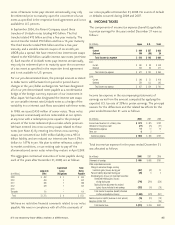
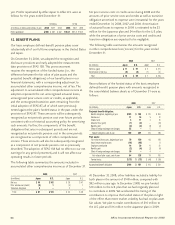
The following table presents the changes in our securities
available for sale classified as Level 3 for the year ended
December 31, 2008.