Aflac 2008 Annual Report Download - page 41
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 41 of the 2008 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
37
It’s no mystery how Aflac makes a difference.
The decrease in our yen-denominated net asset
position resulted from the continuing decline in the
market value of our yen-denominated available-for-
sale investment securities as a result of widening
credit spreads globally.
The table to the right demonstrates the effect of
foreign currency fluctuations by presenting the
dollar values of our yen-denominated assets and
liabilities, and our consolidated yen-denominated
net asset exposure at selected exchange rates as of
December 31.
We are exposed to economic currency risk only
when yen funds are actually converted into dollars.
This primarily occurs when we repatriate funds
from Aflac Japan to Aflac U.S., which is generally
done annually. The exchange rates prevailing at the
time of repatriation will differ from the exchange
rates prevailing at the time the yen profits were
earned. A portion of the repatriation may be used to
service Aflac Incorporated’s yen-denominated notes
payable with the remainder converted into dollars.
Interest Rate Risk
Our primary interest rate exposure is to the impact of
changes in interest rates on the fair value of our investments
in debt and perpetual securities. We use a modified duration
analysis modeling approach, which measures price percentage
volatility, to estimate the sensitivity of the fair values of
our investments to interest rate changes on the debt and
perpetual securities we own. For example, if the current
duration of a debt security or perpetual security is 10, then
the fair value of that security will increase by approximately
10% if market interest rates decrease by 100 basis points,
assuming all other factors remain constant. Likewise, the fair
value of the debt security or perpetual security will decrease
by approximately 10% if market interest rates increase by 100
basis points, assuming all other factors remain constant. We
believe a principal cause of the increase in gross unrealized
losses on securities available for sale is the effect of widening
credit spreads on Aflac Japan’s long-duration invested assets.
The estimated effect of potential increases in interest rates
on the fair values of debt and perpetual securities we own,
notes payable, cross-currency and interest-rate swaps and
our obligation to the Japanese policyholder protection
corporation as of December 31 is shown to the right:
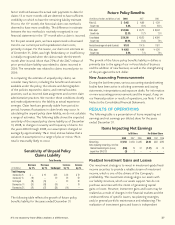
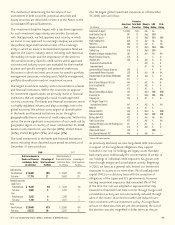
(In millions) 2008 2007
Aflac Japan yen-denominated net assets $ 2,528 $ 2,415
Parent Company yen-denominated net liabilities (1,876) (1,496)
Consolidated yen-denominated net assets subject
to foreign currency translation fluctuations $ 652 $ 919
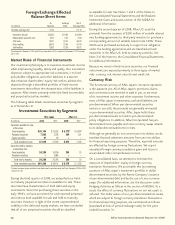
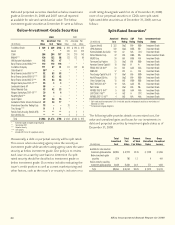
Dollar Value of Yen-Denominated Assets and
Liabilities at Selected Exchange Rates
(In millions) December 31, 2008 December 31, 2007
Yen/dollar exchange rates 76.03 91.03* 106.03 99.15 114.15* 129.15
Yen-denominated financial
instruments:
Assets:
Securities available for sale:
Fixed maturities $ 31,145 $ 26,013 $ 22,333 $ 23,190 $ 20,143 $ 17,803
Perpetual securities 9,343 7,804 6,700 4,211 3,658 3,233
Equity securities 26 22 19 32 28 25
Securities held to maturity:
Fixed maturities 29,018 24,236 20,808 19,341 16,799 14,848
Perpetual securities – – – 4,588 3,985 3,522
Cash and cash equivalents 456 381 327 369 321 284
Other financial instruments 97 80 69 60 52 46
Subtotal 70,085 58,536 50,256 51,791 44,986 39,761
Liabilities:
Notes payable 1,522 1,271 1,091 1,169 1,015 898
Cross-currency swaps 731 610 524 560 487 430
Japanese policyholder
protection corporation 192 161 138 174 151 133
Subtotal 2,445 2,042 1,753 1,903 1,653 1,461
Net yen-denominated
financial instruments 67,640 56,494 48,503 49,888 43,333 38,300
Other yen-denominated
assets 8,605 7,187 6,170 6,310 5,480 4,844
Other yen-denominated
liabilities 75,465 63,029 54,113 55,140 47,894 42,331
Consolidated yen-denominated
net assets subject to foreign
currency fluctuation $ 780 $ 652 $ 560 $ 1,058 $ 919 $ 813
*Actual year-end exchange rate
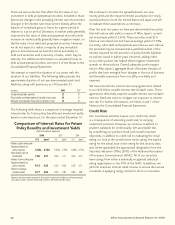
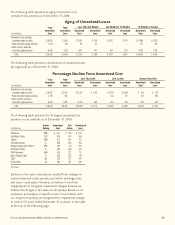
Sensitivity of Fair Values of Financial
Instruments to Interest Rate Changes
2008
2007
+100+
+100
Fair
Basis Fair Basis
(In millions) Value Points Value Points
Debt and perpetual securities:
Fixed-maturity securities:
Yen-denominated $ 49,047 $ 43,556 $ 36,314 $ 32,151
Dollar-denominated 9,048 8,246 10,388 9,505
Perpetual securities:
Yen-denominated 7,804 7,103 7,598 6,889
Dollar-denominated 244 225 431 395
Total debt and
perpetual securities $ 66,143 $ 59,130 $ 54,731 $ 48,940
Notes payable* $ 1,713 $ 1,530 $ 1,452 $ 1,415
Cross-currency and interest-
rate swap liabilities $ 158 $ 151 $ 35 $ 27
Japanese policyholder
protection corporation $ 161 $ 161 $ 151 $ 151
*Excludes capitalized lease obligations