ADT 2013 Annual Report Download - page 136
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 136 of the 2013 ADT annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
FORM 10-K
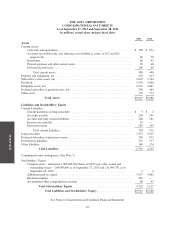
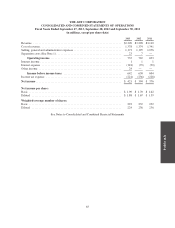
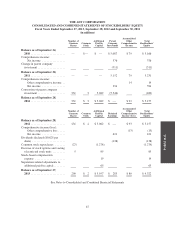
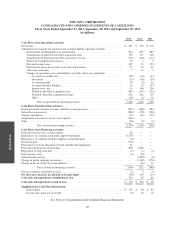
Subscriber System Assets and Related Deferred Costs and Deferred Revenue—The Company considers
security system assets related to its electronic security business in two asset categories: internally generated
subscriber systems (referred to as subscriber system assets) and customer accounts generated through the ADT
dealer program (referred to as dealer intangibles, as further described in the Dealer and Other Amortizable
Intangible Assets, Net section below). Assets associated with internally generated subscriber systems include
installed property and equipment for which the Company retains ownership and deferred costs directly related to
the customer acquisition and system installation. Subscriber system assets represent capitalized equipment and
installation costs incurred to prepare the asset for its intended use. The Company pays property taxes on the
subscriber system assets and upon customer termination, may retrieve such assets. These assets embody a
probable future economic benefit as they generate future monitoring revenue for the Company. Subscriber
system assets, net are recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation. Accumulated depreciation of subscriber
system assets was $2.2 billion and $2.1 billion as of September 27, 2013 and September 28, 2012, respectively.
Depreciation expense relating to subscriber system assets for fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $325 million,
$287 million and $272 million, respectively.
Deferred subscriber acquisition costs, net associated with subscriber system assets represent direct and
incremental selling expenses (i.e. commissions) related to acquiring the customer. Commissions related to up-
front consideration paid by customers in connection with the establishment of the monitoring arrangement are
determined based on a percentage of the up-front fees and do not exceed deferred revenue. Amortization expense
relating to deferred subscriber acquisition costs for fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $123 million, $111
million and $102 million, respectively.
Subscriber system assets and any deferred costs and revenue resulting from the customer acquisition are
accounted for over the expected life of the customer relationship. The Company accounts for subscriber system
assets and related deferred costs and deferred revenue using pools, with separate pools for the components of
subscriber system assets and any related deferred costs and deferred revenue based on the same month and year
of acquisition. The Company depreciates its pooled subscriber system assets and related deferred costs and
deferred revenue using an accelerated method over 15 years. In order to align the depreciation of these assets to
the pattern in which their economic benefits are consumed, the accelerated method utilizes an average declining
balance rate of 245% and converts to a straight-line methodology when the resulting depreciation charge is
greater than that from the accelerated method, resulting in an average depreciation of 59% of the pool within the
first five years, 24% within the second five years and 17% within the final five years.
Dealer and Other Amortizable Intangible Assets, Net—Intangible assets primarily include contracts and
related customer relationships. Certain contracts and related customer relationships are generated from an
external network of independent dealers who operate under the ADT dealer program. These contracts and related
customer relationships are recorded at their contractually determined purchase price. During the initial period of
the customer contract, generally twelve to fifteen months, any cancellation of monitoring service, including those
that result from customer payment delinquencies, results in a chargeback by the Company to the dealer for the
full amount of the contract purchase price. The Company records the amount charged back to the dealer as a
reduction of the intangible assets.
Intangible assets arising from the ADT dealer program described above are amortized in pools determined
by the same month and year of contract commencement on an accelerated basis over the period and pattern of
economic benefit that is expected to be obtained from the customer relationship. The estimated useful life of
dealer intangibles is 15 years. The accelerated method for amortizing these intangible assets utilizes an average
declining balance rate of 300% and converts to a straight-line methodology when the resulting amortization
charge is greater than that from the accelerated method, resulting in an average amortization of 67% of the pool
within the first five years, 22% within the second five years and 11% within the final five years.
Other amortizable intangible assets are amortized on a straight-line basis over 4 to 40 years. The Company
evaluates the amortization methods and remaining useful lives of intangible assets on a periodic basis to determine
whether events and circumstances warrant a revision to the amortization method or remaining useful lives.
72