Volvo 1999 Annual Report Download - page 41
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 41 of the 1999 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
39
earnings capacity in more mature portfolios. The British short-term leasing market
remained under pressure, with resulting stiff competition and falling prices.
The restructuring of Volvo’s sales-financing operations in Brazil was completed
during the year and a positive result was reported.
Provision for risks
Provision is made for both credit risks and residual-value risks to the degree that
residual-value risks are attributable to the sales-financing company. For customers
unable to fulfill their contractual obligations, specific provisions for credit risks are
made based on an individual assessment of each contract. In addition, in accord-
ance with established policies, provisions are made for estimated credit and
residual value losses for each sales-financing company, based on historical data
and anticipated future risk.
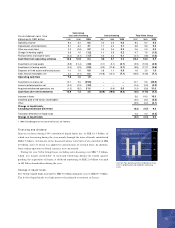
Provisions for estimated credit and residual value losses amounted to 1.3% (2.1
excluding Cars) of the credit portfolio at year-end 1999. In addition, there were
provisions for individual contracts at year-end pertaining to 1.6% of the credit
portfolio (1.5 excluding Cars). Realized credit losses in 1999 amounted to 0.40%
(0.27 excluding Cars).
Because sales-financing operations involve considerable financial exposure in
individual countries, a central provision of SEK 95 M (225) has also been built up.
Decreases in central provisions in 1999 were a result of the sale of Volvo Cars and
did not affect income from sales-financing operations. The central provision
amounted to 0.2% (0.2% excluding Cars) of the credit portfolio at year-end 1999.
New business unit for Volvo’s financing operations
Financing operations are increasingly important for the Volvo Group. In order to
improve financing support to the business areas and Volvo's customers, Volvo’s
entire financing operations are being consolidated in a new Groupwide business
unit, Finance which was formed at year-end 1999. The new unit will include all of
Volvo’s sales-financing operations, including Volvo Finance, Volvo Treasury and
Volvia.
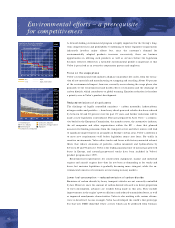
Risk exposure
Parts of the sales-finance operations
give rise to specific credit and
residual-value risks.
Credit risk in sales financing
The credit risk in sales financing is
distributed among a large number of
individual custom ers and dealers.
Collateral is provided in the form of
the products being financed. When
issuing credit, an effort is m ade to
balance risk exposure and expected
yield. Operations are governed by
com mon policies for credits and by
rules for classifying custom ers. The
credit portfolio should be distributed
properly am ong different categories
of custom ers and different industries.
Credit risks are m anaged through
active m onitoring and follow-up
routines and, in appropriate cases,
procedures for repossessing products.
Allocations are also made to credit-
risk reserves.
Residual-value risk in sales
financing
Residual-value risk is attributable
prim arily to contracts involving
operational leasing. It com prises the
risk that the leasing object, at the
end of the operational leasing
contract, has another residual value
than foreseen when the contract was
entered. This may force the lessor to
dispose of products at a loss. Residual-
value risk s are m anaged through
solid knowledge of the m arket, know-
ledge of product and price trends,
and program s supporting the value
of second-hand products. Provisions
are also made in residual-value re-
serves for any differences between
anticipated and actual residual values.
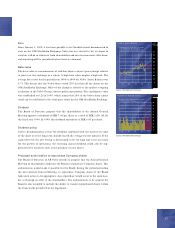
Interest-rate and liquidity risk
in sales financing
Changes in interest rates during the
period covered by a contract can
affect incom e. Therefore, efforts are
made to match the fixed-interest rate
periods for borrowing and lending.
The degree of m atching at year-end
1999 was about 93%
In a corresponding m anner, the
maturity of the borrowing shall
correlate with the maturity of the
outstanding contract. This degree of
matching was also about 91% at
year-end 1999.