Burger King 2013 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2013 Burger King annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
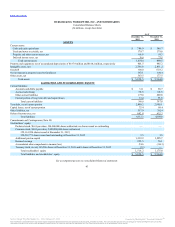
Equity investments in which we hold at least a 20% ownership interest or have significant influence over the investee but not control over the investee are
accounted for using the equity method and are included in other assets, net in our consolidated balance sheets. We also have equity investments in which our
ownership interest is less than 20% that are accounted for using the equity method because we have a significant influence over the investee. Our share of
investee net income or loss is classified as a component of other income (expense), net in our consolidated statements of operations. The difference between the
carrying value of our equity investment and the underlying equity in the historical net assets of the investee is accounted for as if the investee were a
consolidated subsidiary. Accordingly, the carrying value difference is amortized over the estimated lives of the assets of the investee to which such difference
would have been allocated if the equity investment were a consolidated subsidiary. To the extent the carrying value difference represents goodwill an indefinite
lived assets, it is not amortized. We did not record basis difference amortization related to equity method investments for 2013, 2012 and 2011. We evaluate
our investments in equity method investments for impairment whenever events occur or circumstances change in a manner that indicates our investment may
not be recoverable. We did not record impairment charges related to equity method investments for 2013, 2012 and 2011.
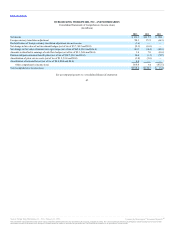
Other comprehensive income (loss) refers to revenues, expenses, gains and losses that are included in comprehensive income (loss), but are excluded
from net income (loss) as these amounts are recorded directly as an adjustment to stockholders’ equity, net of tax. Our other comprehensive income (loss) is
comprised of unrealized gains and losses on foreign currency translation adjustments, unrealized gains and losses on hedging activity, net of tax, and
minimum pension liability adjustments, net of tax.
Gains or losses resulting from changes in the fair value of derivatives are recognized in earnings or recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) and
recognized in the consolidated statements of operations when the hedged item affects earnings, depending on the purpose of the derivatives and whether they
qualify for, and we have applied, hedge accounting treatment.
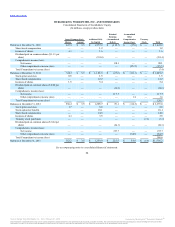
When applying hedge accounting, our policy is to designate, at a derivative’s inception, the specific assets, liabilities or future commitments being
hedged, and to assess the hedge’s effectiveness at inception and on an ongoing basis. We may elect not to designate the derivative as a hedging instrument
where the same financial impact is achieved in the financial statements. We do not enter into or hold derivatives for speculative purposes.
Certain assets and liabilities are not measured at fair value on an ongoing basis but are subject to fair value adjustment in certain circumstances. These
items primarily include long-lived assets, goodwill and intangible assets for which fair value is determined as part of the related impairment tests and asset
retirement obligations initially measured at fair value. At December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012, there were no significant adjustments to fair value or fair
value measurements required for non-financial assets or liabilities.
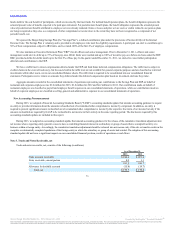
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market
participants in the principal market, or if none exists, the most advantageous market, for the specific asset or liability at the measurement date (the exit price).
The fair value should be based on assumptions that market participants would use when pricing the asset or liability. The fair values are assigned a level
within the fair value hierarchy, depending on the source of the inputs into the calculation, as follows:
Level 1 Observable inputs that reflect quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2 Inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability either directly or indirectly.
Level 3 Unobservable inputs reflecting management’s own assumptions about the inputs used in pricing the asset or liability.
70
Source: Burger King Worldwide, Inc., 10-K, February 21, 2014 Powered by Morningstar® Document Research℠
The information contained herein may not be copied, adapted or distributed and is not warranted to be accurate, complete or timely. The user assumes all risks for any damages or losses arising from any use of this
information, except to the extent such damages or losses cannot be limited or excluded by applicable law. Past financial performance is no guarantee of future results.