Burger King 2012 Annual Report Download - page 114
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 114 of the 2012 Burger King annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
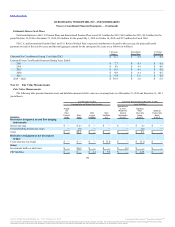
During 2012, we entered into cross-currency rate swaps with an aggregate notional value of $430 million to hedge a portion of the net investment in a
Swiss subsidiary, Burger King Europe GmbH. A total notional value of $230 million of these swaps are contracts to exchange quarterly fixed-rate payments
we make in Euros for quarterly fixed-rate payments we receive in US dollars and mature on October 19, 2016. A total notional value of $200 million of these
swaps are contracts to exchange quarterly floating-rate payments we make in Euros for quarterly floating-rate payments we receive in U.S. Dollars and mature
on September 28, 2017. Changes in the fair value of these instruments are immediately recognized in AOCI to offset the change in the carrying amount of the
net investment being hedged.
Changes in marked-to-market values of these hedges reflected in AOCI were an after-tax loss of $6.6 million at December 31, 2012.
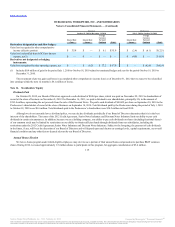
During 2012, we entered into three forward-starting interest rate swaps with a total notional value of $2.3 billion to hedge the variability of forecasted
interest payments attributable to changes in LIBOR. The forward-starting interest rate swaps effectively fix LIBOR on $1.0 billion of floating-rate debt
beginning 2015 and an additional $1.3 billion of floating-rate debt starting 2016. The hedges have a seven year maturity. We account for these hedges as cash
flow hedges, and as such, the effective portion of unrealized changes in market value has been recorded in AOCI and is reclassified to income during the
period in which the hedge transaction affects earnings. Gain and losses from hedge ineffectiveness are recognized in current earnings.
In connection with the 2010 Transactions, interest rate swaps with a notional value of $500 million were terminated. The remaining interest rate swaps
that were not terminated by counterparties had a notional value of $75 million and expired on September 30, 2011.
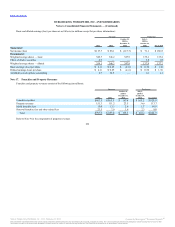
From time to time, we enter into foreign currency forward contracts to economically hedge the remeasurement of certain foreign currency-denominated
intercompany loans receivable and other foreign-currency denominated assets recorded in our consolidated balance sheets. The forward currency forward
contracts are not designated as hedging instruments. Gains and losses on foreign currency forward contracts are recognized in other (income) expense, net and
are offset by the gains or losses resulting from the settlement of the underlying foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities. At December 31, 2012, we
had four foreign currency forward contracts with a total notional amount of $64.8 million maturing in 2013. At December 31, 2011, we had no foreign
currency forward contracts outstanding.
By entering into derivative instrument contracts, we are exposed to counterparty credit risk. Counterparty credit risk is the failure of the counterparty to
perform under the terms of the derivative contract. When the fair value of a derivative contract is in an asset position, the counterparty has a liability to us,
which creates credit risk for us. We attempt to minimize this risk by selecting counterparties with investment grade credit ratings and regularly monitoring our
market position with each counterparty.
113
Source: Burger King Worldwide, Inc., 10-K, February 22, 2013 Powered by Morningstar® Document Research℠
The information contained herein may not be copied, adapted or distributed and is not warranted to be accurate, complete or timely. The user assumes all risks for any damages or losses arising from any use of this
information, except to the extent such damages or losses cannot be limited or excluded by applicable law. Past financial performance is no guarantee of future results.