Avon 2014 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
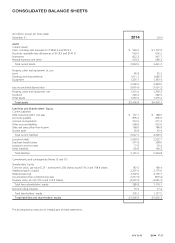
Please find page 82 of the 2014 Avon annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(U.S. dollars in millions, except per share and share data)
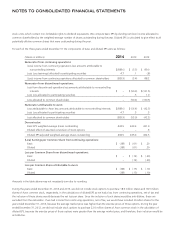
NOTE 1. Description of the Business and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Business
When used in these notes, the terms “Avon,” “Company,” “we,” “our” or “us” mean Avon Products, Inc.
We are a global manufacturer and marketer of beauty and related products. Our business is conducted worldwide, primarily in one channel,
direct selling. Our reportable segments are based on geographic operations in four regions: Latin America; Europe, Middle East & Africa;
North America; and Asia Pacific. Our product categories are Beauty and Fashion & Home. Beauty consists of skincare (which includes
personal care), fragrance and color (cosmetics). Fashion & Home consists of fashion jewelry, watches, apparel, footwear, accessories, gift and
decorative products, housewares, entertainment and leisure products, children’s products and nutritional products. Sales are made to the
ultimate consumer principally by independent Representatives.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Avon and our majority and wholly-owned subsidiaries. Intercompany balances
and transactions are eliminated.
Use of Estimates
We prepare our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the
United States of America, or GAAP. In preparing these statements, we are required to use estimates and assumptions that affect the
reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the
reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates and
assumptions. On an ongoing basis, we review our estimates, including those related to allowances for sales returns, allowances for doubtful
accounts receivable, provisions for inventory obsolescence, the determination of discount rate and other actuarial assumptions for pension
and postretirement benefit expenses, restructuring expense, income taxes and tax valuation allowances, share-based compensation, loss
contingencies and the evaluation of goodwill, intangible assets and capitalized software for potential impairment.
Foreign Currency
Financial statements of foreign subsidiaries operating in other than highly inflationary economies are translated at year-end exchange rates
for assets and liabilities and average exchange rates during the year for income and expense accounts. The resulting translation adjustments
are recorded within accumulated other comprehensive loss (“AOCI”). Gains or losses resulting from the impact of changes in foreign
currency rates on assets and liabilities denominated in a currency other than the functional currency are recorded in other expense, net.
For financial statements of Avon subsidiaries operating in highly inflationary economies, the United States (“U.S.”) dollar is required to be
used as the functional currency. At December 31, 2014, Venezuela was the only Avon subsidiary considered to be operating in a highly
inflationary economy. Highly inflationary accounting requires monetary assets and liabilities, such as cash, receivables and payables, to be
remeasured into U.S. dollars at the current exchange rate at the end of each period with the impact of any changes in exchange rates being
recorded in income. We record the impact of changes in exchange rates on monetary assets and liabilities in other expense, net. Similarly,
deferred tax assets and liabilities are remeasured into U.S. dollars at the current exchange rates; however, the impact of changes in exchange
rates is recorded in income taxes in the Consolidated Statements of Income. Non-monetary assets and liabilities, such as inventory, property,
plant and equipment and prepaid expenses are recorded in U.S. dollars at the historical rates at the time of acquisition of such assets or
liabilities.
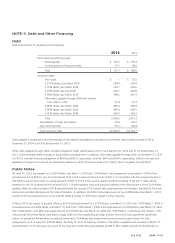
Venezuela Currency
We account for Venezuela as a highly inflationary economy. In February 2014, the Venezuelan government announced a foreign exchange
system (“SICAD II”) which began operating on March 24, 2014. There are multiple legal mechanisms in Venezuela to exchange currency. As
SICAD II represented the rate which better reflected the economics of Avon Venezuela’s business activity, we concluded that we should
utilize the SICAD II exchange rate to remeasure our Venezuelan operations effective March 31, 2014. As a result of the change to the SICAD
II rate, which caused the recognition of a devaluation of approximately 88% as compared to the official exchange rate we used previously,
we recorded an after-tax loss of $41.8 ($53.7 in other expense, net, and a benefit of $11.9 in income taxes) in the first quarter of 2014,
primarily reflecting the write-down of monetary assets and liabilities. In addition, as a result of using the historical U.S. dollar cost basis of
non-monetary assets, such as inventories, these assets continued to be remeasured, following the change to the SICAD II rate, at the