Allstate 2012 Annual Report Download - page 216
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 216 of the 2012 Allstate annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
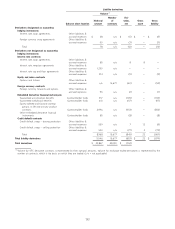
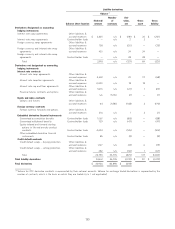
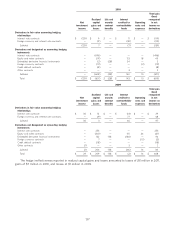
Financial liabilities
December 31, 2011 December 31, 2010
($ in millions)
Carrying Fair Carrying Fair
value value value value
Contractholder funds on investment contracts $ 30,192 $ 30,499 $ 36,163 $ 35,194
Long-term debt 5,908 6,312 5,908 6,325
Liability for collateral 462 462 484 484
The fair value of contractholder funds on investment contracts is based on the terms of the underlying contracts
utilizing prevailing market rates for similar contracts adjusted for the Company’s own credit risk. Deferred annuities
included in contractholder funds are valued using discounted cash flow models which incorporate market value margins,
which are based on the cost of holding economic capital, and the Company’s own credit risk. Immediate annuities
without life contingencies and fixed rate funding agreements are valued at the present value of future benefits using
market implied interest rates which include the Company’s own credit risk.
The fair value of long-term debt is based on market observable data (such as the fair value of the debt when traded
as an asset) or, in certain cases, is determined using discounted cash flow calculations based on current interest rates
for instruments with comparable terms and considers the Company’s own credit risk. The liability for collateral is valued
at carrying value due to its short-term nature.
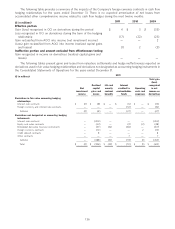
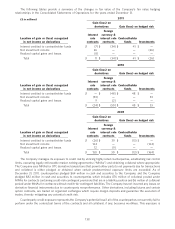
7. Derivative Financial Instruments and Off-balance-sheet Financial Instruments
The Company uses derivatives to manage risks with certain assets and liabilities arising from the potential adverse
impacts from changes in risk-free interest rates, negative equity market valuations, increases in credit spreads and
foreign currency fluctuations, and for asset replication. The Company does not use derivatives for speculative purposes.
Property-Liability uses interest rate swaps, swaptions, futures and options to manage the interest rate risks of
existing investments and to reduce exposure to rising or falling interest rates. Portfolio duration management is a risk
management strategy that is principally employed by Property-Liability wherein financial futures and interest rate swaps
are utilized to change the duration of the portfolio in order to offset the economic effect that interest rates would
otherwise have on the fair value of its fixed income securities. Equity index futures and options are used by Property-
Liability to offset valuation losses in the equity portfolio during periods of declining equity market values. Credit default
swaps are typically used to mitigate the credit risk within the Property-Liability fixed income portfolio. Property-Liability
uses futures to hedge the market risk related to deferred compensation liability contracts and forward contracts to
hedge foreign currency risk associated with holding foreign currency denominated investments and foreign operations.
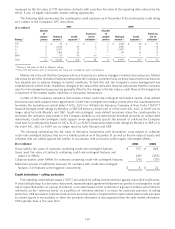
Asset-liability management is a risk management strategy that is principally employed by Allstate Financial to
balance the respective interest-rate sensitivities of its assets and liabilities. Depending upon the attributes of the assets
acquired and liabilities issued, derivative instruments such as interest rate swaps, caps, floors, swaptions and futures are
utilized to change the interest rate characteristics of existing assets and liabilities to ensure the relationship is
maintained within specified ranges and to reduce exposure to rising or falling interest rates. Allstate Financial uses
financial futures and interest rate swaps to hedge anticipated asset purchases and liability issuances and futures and
options for hedging the equity exposure contained in its equity indexed life and annuity product contracts that offer
equity returns to contractholders. In addition, Allstate Financial uses interest rate swaps to hedge interest rate risk
inherent in funding agreements. Allstate Financial uses foreign currency swaps and forward contracts primarily to
reduce the foreign currency risk associated with issuing foreign currency denominated funding agreements and holding
foreign currency denominated investments. Credit default swaps are also typically used to mitigate the credit risk within
the Allstate Financial fixed income portfolio.
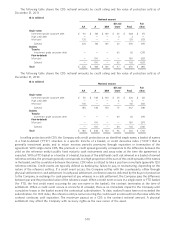
Asset replication refers to the ‘‘synthetic’’ creation of assets through the use of derivatives and primarily investment
grade host bonds to replicate securities that are either unavailable in the cash markets or more economical to acquire in
synthetic form. The Company replicates fixed income securities using a combination of a credit default swap and one or
more highly rated fixed income securities to synthetically replicate the economic characteristics of one or more cash
market securities. The Company also creates ‘‘synthetic’’ exposure to equity markets through the use of exchange
traded equity index future contracts and an investment grade host bond.
The Company also has derivatives embedded in non-derivative host contracts that are required to be separated
from the host contracts and accounted for at fair value. The Company’s primary embedded derivatives are equity
options in life and annuity product contracts, which provide equity returns to contractholders; equity-indexed notes
130