Singapore Airlines 2002 Annual Report Download - page 69
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 69 of the 2002 Singapore Airlines annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
SIA Annual Report 01/02 69
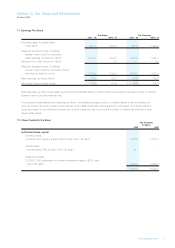
Notes to the Financial Statements
31 March 2002
2 Accounting Policies (continued)
(m) Deferred taxation
Deferred tax is provided, using the liability method, on all temporary differences at the balance sheet date between the tax bases
of assets and liabilities and their carrying amounts for financial reporting purposes.
Additionally the Group’s deferred tax liabilities include all taxable temporary differences associated with investments in subsidiary,
joint venture and associated companies, except where the timing of the reversal of the temporary differences can be controlled
and it is probable that the temporary differences will not reverse in the foreseeable future.
Deferred tax assets are recognised for all deductible temporary differences, carry forward of unused tax assets and losses, to the
extent that it is probable that taxable profit will be available against which the deductible temporary differences, carry forward of
unused tax assets and losses, can be utilized. For deductible temporary differences associated with the Group’s investments in
subsidiary, joint venture and associated companies, deferred tax assets are only recognized to the extent that it is probable that
the temporary differences will reverse in the foreseeable future and taxable profit will be available against which the temporary
difference can be utilized.
The carrying amount of deferred tax assets is reviewed at each balance sheet date and reduced to the extent that it is no longer
probable that sufficient taxable profits will be available to allow all or part of the deferred tax assets to be utilized.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured at the tax rates that are expected to apply to the period when the asset is realized
or the liability is settled, based on tax rates (and tax laws) that have been enacted at the balance sheet date.
(n) Loans and borrowings
Loans, notes payable and other borrowings are recognized at cost.
(o) Aircraft maintenance and overhaul costs
The Company recognizes aircraft maintenance and overhaul expenses on an incurred basis.
(p) Employee Benefits
Equity compensation plan
The Group has in place the Singapore Airlines Limited Employee Share Option Plan, the Singapore Airport Terminal Services
Limited Employee Share Option Plan and the SIA Engineering Company Limited Employee Share Option Plan for granting of share
options to senior executives and all other employees. There are no charges to the profit and loss account upon the grant or
exercise of the options. The exercise price approximates the market value of the shares at the date of grant. Details of the plans
are disclosed in Note 31 to the financial statements.
Defined contribution plan
As required by law, the companies in Singapore make contributions to the state pension scheme, the Central Provident Fund
(CPF). Certain of the Group’s companies and overseas stations outside Singapore make contributions to their respective
countries’ pension schemes. Such contributions are recognized as compensation expenses in the same period as the
employment that gave rise to the contributions.
Defined benefit plan
The Company contributes to several defined benefit pension and other post employment benefit plans for employees stationed in
certain overseas countries. The cost of providing benefits includes the company contribution for the year plus any unfunded
liabilities under the plans, which is determined separately for each plan. Contributions to the plans over the expected average
remaining working lives of the employees participating in the plans are expensed off.