Pep Boys 2013 Annual Report Download - page 116
Download and view the complete annual report
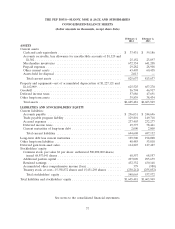
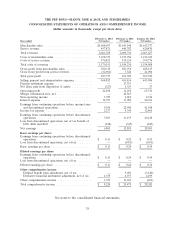
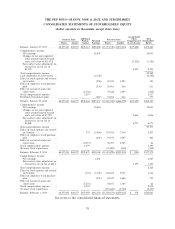
Please find page 116 of the 2013 Pep Boys annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.THE PEP BOYS—MANNY, MOE & JACK AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Years ended February 1, 2014, February 2, 2013 and January 28, 2012
NOTE 1—SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (Continued)
TRADE PAYABLE PROGRAM LIABILITY The Company has a trade payable program which is
funded by various bank participants who have the ability, but not the obligation, to purchase account
receivables owed by the Company directly from its suppliers. The Company, in turn, makes the
regularly scheduled full supplier payments to the bank participants.
INCOME TAXES The Company uses the asset and liability method of accounting for income
taxes. Deferred income taxes are determined based upon enacted tax laws and rates applied to the
differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities.
The Company recognizes taxes payable for the current year, as well as deferred tax assets and
liabilities for the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the Company’s
financial statements or tax returns. The Company must assess the likelihood that any recorded deferred
tax assets will be recovered against future taxable income. To the extent the Company believes it is
more likely than not that the asset will not be recoverable, a valuation allowance must be established.
To the extent the Company establishes a valuation allowance or changes the allowance in a future
period, income tax expense will be impacted.
In evaluating income tax positions, the Company records liabilities for potential exposures. These
tax liabilities are adjusted in the period actual developments give rise to such change. Those
developments could be, but are not limited to, settlement of tax audits, expiration of the statute of
limitations, and changes in the tax code and regulations, along with varying application of tax policy
and administration within those jurisdictions. Refer to Note 8, ‘‘Income Taxes,’’ for further discussion of
income taxes and changes in unrecognized tax benefit.
SALES TAXES The Company presents sales net of sales taxes in its consolidated statements of
operations.
REVENUE RECOGNITION The Company recognizes revenue from the sale of merchandise at
the time the merchandise is sold and the product is delivered to the customer, net of an allowance for
estimated future returns. Service revenues are recognized on completion of the service. Service revenue
consists of the labor charged for installing merchandise or maintaining or repairing vehicles, excluding
the sale of any installed parts or materials. The Company records revenue net of an allowance for
estimated future returns. The Company establishes reserves for sales returns and allowances based on
current sales levels and historical return rates. Revenue from gift card sales is recognized on gift card
redemption. The Company’s gift cards do not have expiration dates. The Company recognizes breakage
on gift cards when, among other things, sufficient gift card history is available to estimate potential
breakage and the Company determines there are no legal obligations to remit the value of unredeemed
gift cards to the relevant jurisdictions. Estimated gift card breakage revenue is immaterial for all
periods presented.
The Company’s Customer Loyalty program allows members to earn points for each qualifying
purchase. Points earned allow members to receive a certificate that may be redeemed on future
purchases within 120 days of issuance. The retail value of points earned by loyalty program members is
included in accrued liabilities as deferred income and recorded as a reduction of revenue at the time
the points are earned, based on the historic and projected rate of redemption. The Company
recognizes deferred revenue and the cost of the free products distributed to loyalty program members
44