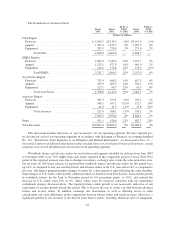
Nike 2003 Annual Report Download - page 32
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 32 of the 2003 Nike annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.We use VaR to monitor the foreign exchange risk of our foreign currency forward and foreign currency option
derivative instruments only. The VaR determines the maximum potential one-day loss in the fair value of these
foreign exchange rate-sensitive financial instruments. The VaR model estimates assume normal market conditions
and a 95% confidence level. There are various modeling techniques that can be used in the VaR computation. Our
computations are based on interrelationships between currencies and interest rates (a “variance/co-variance”
technique). These interrelationships are a function of foreign exchange currency market changes and interest rate
changes over the preceding one year. The value of foreign currency options does not change on a one-to-one basis
with changes in the underlying currency rate. We adjusted the potential loss in option value for the estimated
sensitivity (the “delta” and “gamma”) to changes in the underlying currency rate. This calculation reflects the
impact of foreign currency rate fluctuations on the derivative instruments only, and hence does not include the
impact of such rate fluctuations on the underlying based transactions that are anticipated transactions, firm
commitments, cash balances and accounts and loans receivable and payable denominated in foreign currencies from
the VaR calculation, including those which are hedged by these instruments.
The VaR model is a risk analysis tool and does not purport to represent actual losses in fair value that we will
incur, nor does it consider the potential effect of favorable changes in market rates. It also does not represent the full
extent of the possible loss that may occur. Actual future gains and losses will differ from those estimated because of
changes or differences in market rates and interrelationships, hedging instruments and hedge percentages, timing
and other factors.
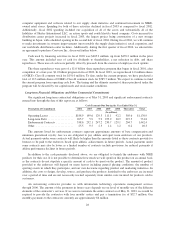
The estimated maximum one-day loss in fair value on our foreign currency sensitive financial instruments,
derived using the VaR model, was $21.0 million and $13.7 million at May 31, 2003 and May 31, 2002, respectively.
The increase in VaR as of May 31, 2003 occurred due to the effect of currency volatility on existing trades on the
May 31, 2003 VaR computation versus the effect of currency volatility on existing trades on the May 31, 2002 VaR
computation. Such a hypothetical loss in fair value of our derivatives would be offset by increases in the value of the
underlying transactions being hedged. The average monthly change in the fair values of foreign currency forward
and foreign currency option derivative instruments was $43.3 million and $42.9 million for fiscal 2003 and fiscal
2002, respectively.
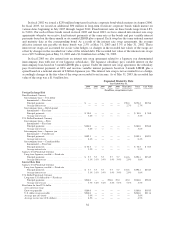
Details of other market-sensitive financial instruments and derivative financial instruments not included in the
VaR calculation above are provided in the table below, except the interest rate swaps which are described below.
These instruments include intercompany loans denominated in foreign currencies, fixed interest rate Japanese yen
denominated debt, fixed interest rate U.S. dollar denominated debt, cross-currency swaps, and interest rate swaps.
For debt obligations, the table presents principal cash flows and related weighted average interest rates by expected
maturity dates. We have excluded the cross-currency swaps from the foreign exchange risk category because these
instruments eliminate all foreign currency exposure in the cash flows of a euro denominated intercompany loan. We
have included these cross-currency swaps in the interest rate risk category but excluded the related intercompany
loan from this category because the intercompany interest eliminates in consolidation. For the cross-currency swaps
the table presents both the euro swap payable and U.S. dollar swap receivable and the respective pay and receive
interest rates. All information is presented in millions of U.S. dollars, except interest rates.
Intercompany loans and related interest amounts eliminate in consolidation. Intercompany loans are generally
hedged against foreign exchange risk through the use of forward contracts and swaps with third parties.
The fixed interest rate Japanese yen denominated debts were issued by and are accounted for by two of our
Japanese subsidiaries. Accordingly, the monthly remeasurement of these instruments due to changes in foreign
exchange rates is recognized in accumulated other comprehensive loss upon the consolidation of these subsidiaries.
There were no significant changes in debt or cross-currency swap market risks during fiscal 2003. The U.S. dollar
fair values of intercompany loans denominated in foreign currencies was $649.4 million at May 31, 2002, which is the
same as the carrying values of the loans prior to their elimination. The U.S. dollar fair value of the fixed rate Japanese
yen denominated debt that was outstanding at May 31, 2002 was $207.4 million versus a carrying value of $181.4
million at that date. The U.S. dollar fair values of the fixed rate U.S. dollar denominated debt, the euro swap payable
and the U.S. dollar swap receivable as of May 31, 2002 were $516.5 million, $196.2 million and $267.9 million,
respectively, versus carrying values of $499.8 million, $188.8 million and $250.0 million, respectively, at that date.
31