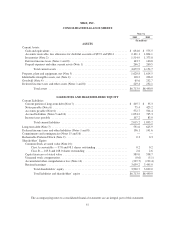
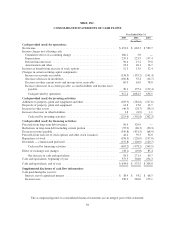
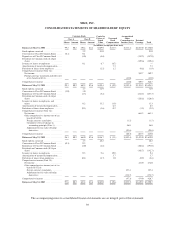
Nike 2003 Annual Report Download - page 31
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 31 of the 2003 Nike annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.rates would decrease. Changes in our long-term debt rating would not trigger acceleration of maturity of any then
outstanding borrowings or any future borrowings under the committed credit facilities. However, under these
committed credit facilities, we have agreed to various covenants. These covenants include limits on our disposal
of fixed assets and the amount of debt secured by liens we may incur, and set a minimum ratio of net worth to
indebtedness. In the event we were to have any borrowings outstanding under these facilities, failed to meet any
covenant, and were unable to obtain a waiver from a majority of the banks, any borrowings would become
immediately due and payable. As of May 31, 2003, we were in full compliance with each of these covenants and
believe it is unlikely we will fail to meet any of these covenants in the foreseeable future.
Liquidity is also provided by our commercial paper program, under which there was no amount outstanding
at May 31, 2003 and $338.3 million outstanding at May 31, 2002. We currently have short-term debt ratings of
A1 and P1 from Standard and Poor’s Corporation and Moody’s Investor Services, respectively.
We currently believe that cash generated by operations, together with access to external sources of funds as
described above, will be sufficient to meet our operating and capital needs in the foreseeable future.
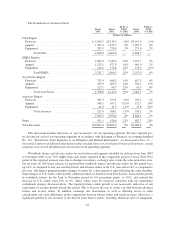
Dividends per share of common stock for fiscal 2003 were $0.54, compared to $0.48 in fiscal 2002. We
have paid a dividend every quarter since February 1984. We review our dividend policy from time to time;
however, based upon current projected earnings and cash flow requirements, we anticipate continuing to pay a
quarterly dividend in the foreseeable future.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
In the normal course of business and consistent with established policies and procedures, we employ a
variety of financial instruments to manage exposure to fluctuations in the value of foreign currencies and interest
rates. It is our policy to utilize these financial instruments only where necessary to finance our business and
manage such exposures; we do not enter into these transactions for speculative purposes.
We are exposed to foreign currency fluctuation as a result of our international sales, production and funding
activities. Our foreign currency risk management objective is to reduce the variability of local entity cash flows
as a result of exchange rate movements. We use forward exchange contracts and options to hedge certain
anticipated but not yet firmly committed transactions as well as certain firm commitments and the related
receivables and payables, including third party or intercompany transactions.
When we begin hedging exposures depends on the nature of the exposure and market conditions. Generally,
all anticipated and firmly committed transactions that are hedged are to be recognized within twelve months,
although at May 31, 2003 we had forward contracts hedging anticipated transactions that will be recognized in as
many as 18 months. The majority of the contracts expiring in more than twelve months relate to the anticipated
purchase of inventory by our European and Japanese subsidiaries. We use forward contracts and cross-currency
swaps to hedge foreign currency denominated payments under intercompany loan agreements. When
intercompany loans are hedged, it is typically for their expected duration. Hedged transactions are principally
denominated in European currencies, Japanese yen, Canadian dollars, Korean won, Mexican pesos and
Australian dollars.
Our earnings are also exposed to movements in short and long-term market interest rates. Our objective in
managing this interest rate exposure is to limit the impact of interest rate changes on earnings and cash flows, and
to reduce overall borrowing costs. To achieve these objectives, we maintain a mix of medium and long-term
fixed rate debt, commercial paper, and bank loans and have entered into interest rate swaps under which we
receive fixed interest and pay variable interest.
Market Risk Measurement
We monitor foreign exchange risk, interest rate risk and related derivatives using a variety of techniques
including a review of market value, sensitivity analysis, and Value-at-Risk (VaR). Our market-sensitive derivative
and other financial instruments, as defined by the SEC, are foreign currency forward contracts, foreign currency
option contracts, cross-currency swaps, interest rate swaps, intercompany loans denominated in foreign currencies,
fixed interest rate U.S. dollar denominated debt, and fixed interest rate Japanese yen denominated debt.
30