HP 2010 Annual Report Download - page 50
Download and view the complete annual report
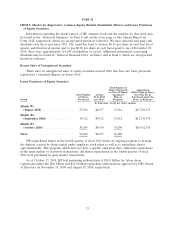
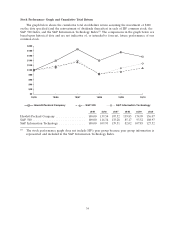
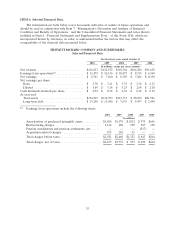
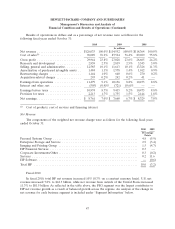
Please find page 50 of the 2010 HP annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
$760 million to approximately $33 billion. In order to evaluate the sensitivity of the fair value
calculations on the goodwill impairment test, we applied a hypothetical 10% decrease to the fair values
of each reporting unit. This hypothetical 10% decrease would result in excess fair value over carrying
value ranging from approximately $360 million to approximately $29 billion for each of HP’s reporting
units.
Restructuring
We have engaged, and may continue to engage, in restructuring actions, which require
management to utilize significant estimates related to the timing and the expenses for severance and
other employee separation costs, realizable values of assets made redundant or obsolete, lease
cancellation and other exit costs. If the actual amounts differ from our estimates, the amount of the
restructuring charges could be materially impacted. For a full description of our restructuring actions,
refer to our discussions of restructuring in the Results of Operations section and Note 8 to the
Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8, which are incorporated herein by reference.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
We recognize stock-based compensation expense for all share-based payment awards, net of an
estimated forfeiture rate. We recognize compensation cost for only those shares expected to vest on a
straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the award.
Determining the appropriate fair value model and calculating the fair value of share-based
payment awards requires subjective assumptions, including the expected life of the share-based payment
awards and stock price volatility. We utilize the Black-Scholes option pricing model to value the stock
options granted under our principal option plans. To implement this model, we examined our historical
pattern of option exercises to determine if there were any discernable activity patterns based on certain
employee populations. From this analysis, we identified three employee populations to which to apply
the Black-Scholes model. We determined that implied volatility calculated based on actively traded
options on HP common stock is a better indicator of expected volatility and future stock price trends
than historical volatility.
We issue performance-based restricted units (‘‘PRUs’’) representing hypothetical shares of HP
common stock. Each PRU award reflects a target number of shares that may be issued to the award
recipient. We determine the actual number of shares the recipient receives at the end of a three-year
performance period based on results achieved versus goals based on our annual cash flow from
operations as a percentage of revenue and total shareholder return (‘‘TSR’’) relative to the S&P 500
over the performance period. We use historic volatility for PRU awards as implied volatility cannot be
used when simulating multivariate prices for companies in the S&P 500. We estimate the fair value of
PRUs using the Monte Carlo simulation model, as the TSR modifier contains a market condition. We
update the estimated expense, net of forfeitures, for the cash flow performance against the goal for
that year at the end of each reporting period.
The assumptions used in calculating the fair value of share-based payment awards represent
management’s best estimates, but these estimates involve inherent uncertainties and the application of
management judgment. As a result, if factors change and we use different assumptions, our stock-based
compensation expense could be materially different in the future. In addition, we are required to
estimate the expected forfeiture rate and recognize expense only for those shares expected to vest. If
our actual forfeiture rate is materially different from our estimate, the stock-based compensation
42