Dollar General 2012 Annual Report Download - page 155
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 155 of the 2012 Dollar General annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
10-K
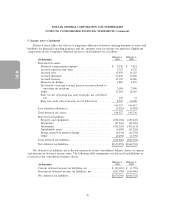
DOLLAR GENERAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
8. Derivative financial instruments (Continued)
risks, including interest rate, liquidity, and credit risk, primarily by managing the amount, sources, and
duration of its debt funding and the use of derivative financial instruments. Specifically, the Company
enters into derivative financial instruments to manage exposures that arise from business activities that
result in the receipt or payment of future known and uncertain cash amounts, the value of which are
determined primarily by interest rates. The Company’s derivative financial instruments are used to
manage differences in the amount, timing, and duration of the Company’s known or expected cash
receipts and its known or expected cash payments principally related to the Company’s borrowings.
The Company is exposed to certain risks arising from uncertainties of future market values caused
by the fluctuation in the prices of commodities. From time to time the Company may enter into
derivative financial instruments to protect against future price changes related to these commodity
prices.
Cash flow hedges of interest rate risk
The Company’s objectives in using interest rate derivatives are to add stability to interest expense
and to manage its exposure to interest rate changes. To accomplish this objective, the Company
primarily uses interest rate swaps as part of its interest rate risk management strategy. Interest rate
swaps designated as cash flow hedges involve the receipt of variable-rate amounts from a counterparty
in exchange for the Company making fixed-rate payments over the life of the agreements without
exchange of the underlying notional amount.
The effective portion of changes in the fair value of derivatives designated and that qualify as cash
flow hedges is recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) (also referred to as ‘‘OCI’’)
and is subsequently reclassified into earnings in the period that the hedged forecasted transaction
affects earnings. These transactions represent the only amounts reflected in Accumulated other
comprehensive income (loss) in the consolidated statements of shareholders’ equity. During the years
ended February 1, 2013, February 3, 2012 and January 28, 2011, such derivatives were used to hedge
the variable cash flows associated with existing variable-rate debt. The ineffective portion of the change
in fair value of the derivatives is recognized directly in earnings.
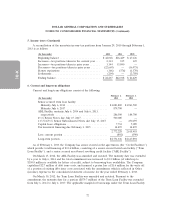
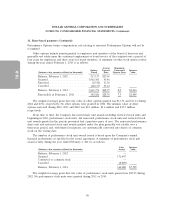
As of February 1, 2013, the Company had three interest rate swaps with a combined notional value
of $875 million that were designated as cash flow hedges of interest rate risk. Amounts reported in
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) related to derivatives will be reclassified to interest
expense as interest payments are made on the Company’s variable-rate debt. During the next 52-week
period, the Company estimates that an additional $3.1 million will be reclassified as an increase to
interest expense for all of its interest rate swaps.
Non-designated hedges of commodity risk
Derivatives not designated as hedges are not speculative and are used to manage the Company’s
exposure to commodity price risk but do not meet strict hedge accounting requirements. Changes in
the fair value of derivatives not designated in hedging relationships are recorded directly in earnings.
As of February 1, 2013, the Company had no such non-designated hedges.
76