Dollar General 2012 Annual Report Download - page 141
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 141 of the 2012 Dollar General annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
10-K
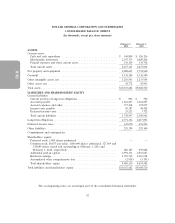
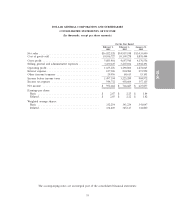
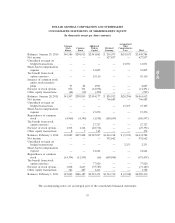
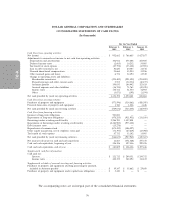
DOLLAR GENERAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
1. Basis of presentation and accounting policies (Continued)
The Company recognizes contingent rental expense when the achievement of specified sales targets
are considered probable, in accordance with applicable accounting standards for contingent rent. The
amount expensed but not paid as of February 1, 2013 and February 3, 2012 was approximately
$7.7 million and $9.4 million, respectively, and is included in Accrued expenses and other in the
consolidated balance sheets.
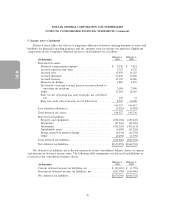
Other liabilities
Noncurrent Other liabilities consist of the following:
February 1, February 3,
(In thousands) 2013 2012
Compensation and benefits ......................... $ 18,404 $ 17,570
Insurance ...................................... 137,451 137,891
Income tax related reserves ......................... 23,383 41,130
Other ......................................... 46,161 32,558
$225,399 $229,149
Amounts reflected as ‘‘other’’ in the table above consist primarily of deferred rent and derivative
liabilities.
Fair value accounting
The Company utilizes accounting standards for fair value, which include the definition of fair
value, the framework for measuring fair value, and disclosures about fair value measurements. Fair
value is a market-based measurement, not an entity-specific measurement. Therefore, a fair value
measurement should be determined based on the assumptions that market participants would use in
pricing the asset or liability. As a basis for considering market participant assumptions in fair value
measurements, fair value accounting standards establish a fair value hierarchy that distinguishes
between market participant assumptions based on market data obtained from sources independent of
the reporting entity (observable inputs that are classified within Levels 1 and 2 of the hierarchy) and
the reporting entity’s own assumptions about market participant assumptions (unobservable inputs
classified within Level 3 of the hierarchy).
Level 1 inputs utilize quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities
that the Company has the ability to access. Level 2 inputs are inputs other than quoted prices included
in Level 1 that are directly or indirectly observable for the asset or liability. Level 2 inputs may include
quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, as well as inputs that are observable for
the asset or liability (other than quoted prices), such as interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and yield
curves that are observable at commonly quoted intervals. Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs for the
asset or liability, which are based on an entity’s own assumptions, as there is little, if any, related
market activity. In instances where the determination of the fair value measurement is based on inputs
from different levels of the fair value hierarchy, the level in the fair value hierarchy within which the
entire fair value measurement falls is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value
measurement in its entirety. The Company’s assessment of the significance of a particular input to the
62