Singapore Airlines 2005 Annual Report Download - page 105
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 105 of the 2005 Singapore Airlines annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SIA Annual Report 04/05 103
Notes to the Financial Statements
31 March 2005
CC
MOD: CN1323
M Y
C K
While every effort has been taken to carry out instruction to customers satisfaction
NO RESPONSIBILITY liablilty will be accepted for errors
CUSTOMERS ARE THEREFOREURGED TO CHECK THOROUGHLY BEFORE
AUTHORISING PRINTRUNS
DALIM
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 OK TS
CC196777 DLMAC13 10.06.2005 150#
1
3col
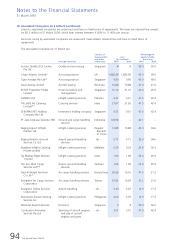
32 Contingent Liabilities (in $ million) (continued)
Others
There are contingent liabilities in respect of insurance and performance bonds, and bank guarantees given by the Group
and the Company at 31 March 2005 amounting to $56.4 million (2004: $64.8 million) and $22.8 million (2004: $28.1
million) respectively.
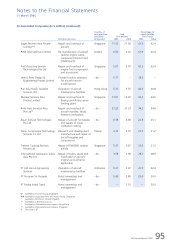
33 Financial Instruments (in $ million)
(a) Financial risk management objectives and policies
The Group operates globally and generates revenue in various currencies. The Group’s airline operations carry certain
financial and commodity risks, including the effects of changes in jet fuel prices, foreign currency exchange rates,
interest rates and the market value of its investments. The Group’s overall risk management approach is to moderate
the effects of such volatility on its financial performance.
Financial risk management policies are periodically reviewed and approved by the Board Finance Committee (“BFC”).
(b) Jet fuel price risk
The Group’s earnings are affected by changes in the price of jet fuel. The Group manages this fuel price risk by using
swap and option contracts and hedging up to 24 months forward. A change in price of one US cent per American
gallon of jet fuel affects the Group’s annual fuel costs by US$14 million, assuming no change in volume of fuel
consumed.
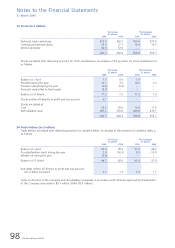
(c) Foreign currency risk
The Group is exposed to the effects of foreign exchange rate fluctuations because of its foreign currency
denominated operating revenues and expenses. For the financial year ended 31 March 2005, these accounted for
68% of total revenue (2003-04: 70%) and 64% of total operating expenses (2003-04: 51%). The Group’s largest
exposures are from USD, Euro, UK Sterling Pound, Swiss Franc, Australian Dollar, New Zealand Dollar, Japanese Yen,
Indian Rupee, Hong Kong Dollar, Chinese Yuan, Korean Won and Malaysian Ringgit. The Group generates a surplus
in all of these currencies, with the exception of USD. The deficit in USD is attributable to capital expenditure, fuel
costs and aircraft leasing costs – all conventionally denominated and payable in USD.
The Group manages its foreign exchange exposure by a policy of matching, as far as possible, receipts and payments
in each individual currency. Surpluses of convertible currencies are sold, as soon as practicable, for USD and SGD.
The Group also uses forward foreign currency contracts to hedge a portion of its future foreign exchange exposure.
Such contracts provide for the Group to sell currencies at predetermined forward rates, buying either USD or SGD
depending on forecast requirements, with settlement dates that range from one month up to one year.
(d) Interest rate risk
The Group’s earnings are also affected by changes in interest rates due to the impact such changes have on interest
income and expense from short-term deposits and other interest-bearing financial assets and liabilities. The majority
of the Group’s interest-bearing financial liabilities with maturities above one year have fixed rates of interest or are
hedged by matching interest-bearing financial assets. Interest rate swaps are used to convert a portion of floating
interest rate obligations in respect of other financial liabilities into fixed interest rate obligations.
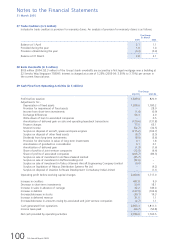
(e) Market price risk
The Group owned $431.4 million (2004: $378.1 million) in quoted equity and non-equity investments at
31 March 2005. The estimated market value of these investments was $435.4 million (2004: $467.6 million) at
31 March 2005.
The market risk associated with these investments is the potential loss resulting from a decrease in market prices.
(f) Counterparty risk
Surplus funds are invested in interest-bearing bank deposits and other high quality short-term liquid investments.
Counterparty risks are managed by limiting aggregated exposure on all outstanding financial instruments to any
individual counterparty, taking into account its credit rating. Such counterparty exposures are regularly reviewed,
and adjusted as necessary. This mitigates the risk of material loss arising in the event of non-performance by
counterparties.