Time Magazine 2014 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2014 Time Magazine annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.TIME WARNER INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
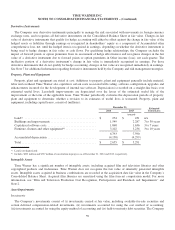
Venezuela Currency
Certain of the Company’s divisions conduct business with third parties located in Venezuela and, as a result, the Company
holds net monetary assets denominated in Venezuelan Bolivares Fuertes (“VEF”) that primarily consist of cash and accounts
receivable. As of December 31, 2014, there were three legal foreign currency exchange systems administered by the
Venezuelan government, each with a different exchange rate: (i) the fixed official government rate as published by the
Central Bank of Venezuela, which as of December 31, 2014 was 6.3 VEF to each U.S. Dollar, (ii) the variable, auction-based
SICAD 1 rate, which as of December 31, 2014 was 12 VEF to each U.S. Dollar and (iii) the variable, transaction-based
SICAD 2 rate, which as of December 31, 2014 was approximately 50 VEF to each U.S. Dollar. Because of Venezuelan
government-imposed restrictions on the exchange of VEF into foreign currency in Venezuela, the Company has not been
able to convert VEF earned in Venezuela into U.S. Dollars through the official government rate. Further, the Company has
not been able to access the SICAD 1 and SICAD 2 exchanges due to government requirements and restrictions on
participation in the exchanges, including a requirement that an entity be domiciled in Venezuela to participate.
Prior to December 31, 2014, the Company used the official government exchange rate to remeasure its VEF-denominated
transactions and balances. This was principally due to the Company’s inability to access the SICAD 1 and SICAD 2
exchange systems, as noted above, as well as a lack of clarity about those exchange systems’ stability and transaction
volume. During the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company considered information about the companies that were able to
access the three exchange systems during 2014 and the fact that the SICAD 1 and SICAD 2 exchanges continued to operate,
as well as the state of the Venezuelan economy, which has been negatively impacted by significantly lower oil prices and
which the Venezuela Central Bank confirmed in late December 2014 had entered a recession. Based on these factors, as of
December 31, 2014, the Company concluded that the SICAD 2 exchange rate was the most appropriate legal exchange rate
for the Company’s business activities conducted in VEF. Accordingly, beginning on December 31, 2014, the Company
began using the SICAD 2 rate to remeasure its VEF-denominated transactions and balances and, for the three months and
year ended December 31, 2014, recognized a pretax foreign exchange loss of $173 million in the Consolidated Statement of
Operations.
Accounting Guidance Adopted in 2014
Share-Based Payment Awards with Performance Targets Attainable After the Requisite Service Period
On July 1, 2014, the Company early adopted guidance that clarifies that a performance target that affects the vesting of an
award payable in shares and that can be met after the requisite service period is a performance condition. Therefore,
compensation expense related to such awards should only be recognized when it becomes probable that the performance
target will be met, which could occur after the requisite service period has been satisfied. The adoption of this guidance did
not have an impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Presentation of Unrecognized Tax Benefits
On January 1, 2014, the Company adopted on a prospective basis guidance requiring a liability related to an unrecognized
tax benefit to be offset against a deferred tax asset for a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss or a tax credit
carryforward if such settlement is required or expected in the event the uncertain tax position is disallowed. In situations in
which a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss or a tax credit carryforward is not available at the reporting date
under the tax law of a jurisdiction or the tax law of a jurisdiction does not require it, and the Company does not intend to use
the deferred tax asset for such purpose, the unrecognized tax benefit would be presented in the financial statements as a
liability and will not be combined with deferred tax assets. The adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact on
the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Accounting Guidance Not Yet Adopted
Revenue Recognition
In May 2014, guidance was issued that establishes a new revenue recognition framework in U.S. GAAP for all companies
and industries. The core principle of the guidance is that an entity should recognize revenue from the transfer of
56