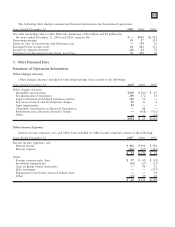
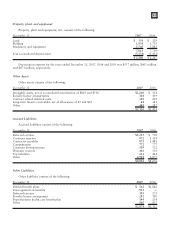
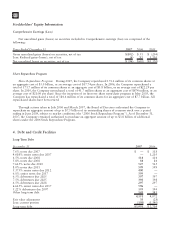
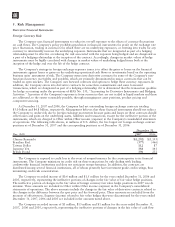
Motorola 2007 Annual Report Download - page 90
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 90 of the 2007 Motorola annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Intangible assets are amortized over their respective estimated useful lives ranging from one to 14 years. The
Company has no intangible assets with indefinite useful lives.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets: Long-lived assets, which include intangible assets, held and used by the
Company are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying
amount of assets may not be recoverable. The Company evaluates recoverability of assets to be held and used by
comparing the carrying amount of an asset (group) to future net undiscounted cash flows to be generated by the
asset (group). If an asset is considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is equal to the amount by
which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the asset’s fair value calculated using a discounted future cash
flows analysis or market comparables. Assets held for sale, if any, are reported at the lower of the carrying amount
or fair value less cost to sell.
Deferred Income Taxes: Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences
attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and
their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carry forwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are
measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary
differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in
tax rates is recognized in the period that includes the enactment date. In assessing the realizability of the deferred
tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will
not be realized. A valuation allowance is recorded for the portion of the deferred tax assets that are not expected
to be realized based on the level of historical taxable income, projections for future taxable income over the
periods in which the temporary differences are deductible and allowable tax planning strategies. Beginning
January 1, 2007, the Company recognizes the effect of income tax positions only if sustaining those positions is
more likely than not. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which a change in
judgment occurs. Prior to January 1, 2007, the Company recognized the effect of income tax positions only if such
positions were probable of being sustained.
The Company records interest related to unrecognized tax benefits in Interest expense and penalties in Selling,
general and administrative expenses in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations.
Finance Receivables: Finance receivables include trade receivables where contractual terms of the note
agreement are greater than one year. Finance receivables are considered impaired when management determines
collection of all amounts due according to the contractual terms of the note agreement, including principal and
interest, is no longer probable. Impaired finance receivables are valued based on the present value of expected
future cash flows, discounted at the receivable’s effective rate of interest, or the fair value of the collateral if the
receivable is collateral dependent. Interest income and late fees on impaired finance receivables are recognized only
when payments are received. Previously impaired finance receivables are no longer considered impaired and are
reclassified to performing when they have performed under a workout or restructuring for four consecutive
quarters.
Foreign Currency: Certain of the Company’s non-U.S. operations use their respective local currency as their
functional currency. Those operations that do not have the U.S. dollar as their functional currency translate assets
and liabilities at current rates of exchange in effect at the balance sheet date and revenues and expenses using the
prior period month-end exchange rates. The resulting translation adjustments are included as a component of Non-
owner changes to equity in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets. For those operations that have the
U.S. dollar as their functional currency, transactions denominated in the local currency are measured into
U.S. dollars using the current rates of exchange for monetary assets and liabilities and historical rates of exchange
for nonmonetary assets. Gains and losses from remeasurement of monetary assets and liabilities are included in
Other included in Other income (expense) within the Company’s consolidated statements of operations.
Derivative Instruments: Gains and losses on hedges of existing assets or liabilities are marked-to-market and
the result is included in Other within Other income (expense) within the Company’s consolidated statements of
operations. Gains and losses on financial instruments that qualify for hedge accounting and are used to hedge firm
future commitments or forecasted transactions are deferred until such time as the underlying transactions are
recognized or recorded immediately when the transaction is no longer expected to occur. Gains or losses on
financial instruments that do not qualify as hedges under Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”)
No. 133, “Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities” (“SFAS 133”) are recognized
immediately as income or expense.
Earnings Per Share: The Company calculates its basic earnings per share based on the weighted-average
effect of all common shares issued and outstanding. Net earnings is divided by the weighted average common
82