MasterCard 2013 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 68 of the 2013 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
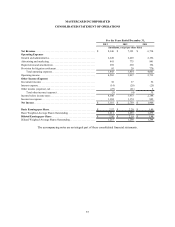
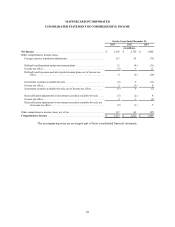
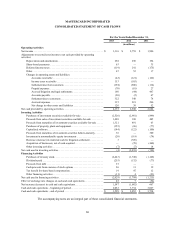
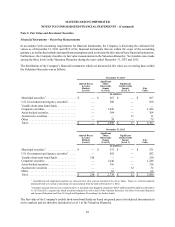
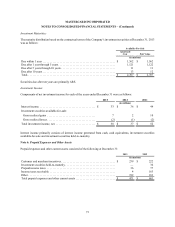
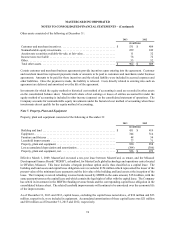
MASTERCARD INCORPORATED
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
64
Deferred income taxes are displayed as separate line items or are included in other current liabilities on the consolidated
balance sheet. Valuation allowances are provided against assets which are not more likely than not to be realized. The
Company recognizes all material tax positions, including uncertain tax positions in which it is more likely than not that
the position will be sustained based on its technical merits and if challenged by the relevant taxing authorities. At each
balance sheet date, unresolved uncertain tax positions are reassessed to determine whether subsequent developments
require a change in the amount of recognized tax benefit. The allowance for uncertain tax positions is recorded in other
current and noncurrent liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet.
The Company records interest expense related to income tax matters as interest expense in its statement of operations.
The Company includes penalties related to income tax matters in the income tax provision. The Company does not
provide for U.S. federal income tax and foreign withholding taxes on undistributed earnings from non-U.S. subsidiaries
when such earnings are intended to be reinvested indefinitely outside of the U.S.
Cash and cash equivalents - Cash and cash equivalents include certain investments with daily liquidity and with a
maturity of three months or less from the date of purchase. Cash equivalents are recorded at cost, which approximates
fair value.
Restricted cash - The Company classifies cash as restricted when the cash is unavailable for withdrawal or usage for
general operations. Restrictions may include legally restricted deposits, contracts entered into with others, or the
Company's statements of intention with regard to particular deposits. In December 2012, the Company made a payment
into a qualified cash settlement fund related to its U.S. merchant class litigation. The Company has presented these
funds as restricted cash for litigation settlement since the use of the funds under the qualified cash settlement fund is
restricted for payment under the settlement agreement. In January 2014, $164 million was returned to MasterCard
from the qualified cash settlement fund related to the opt out merchants and will be reclassified to cash and cash
equivalents. See Note 18 (Legal and Regulatory Proceedings) for further detail.
Fair value - The Company measures certain financial assets and liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis by estimating
the price that would be received upon the sale of an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between
market participants. The Company classifies these recurring fair value measurements into a three-level hierarchy
("Valuation Hierarchy").
The Valuation Hierarchy is based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the
measurement date. A financial instrument's categorization within the Valuation Hierarchy is based upon the lowest
level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The three levels of the Valuation Hierarchy are as
follows:
Level 1-inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities
in active markets.
Level 2-inputs to the valuation methodology include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active
markets, quoted prices for identical assets and liabilities in inactive markets and inputs that are observable for
the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
Level 3-inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and cannot be directly corroborated by
observable market data.
Certain assets and liabilities are measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis. The Company's assets and liabilities
measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis include property, plant and equipment, nonmarketable equity investments,
goodwill and other intangible assets. These assets are subject to fair value adjustments in certain circumstances, such
as when there is evidence of impairment.
The valuation methods for goodwill and other intangible assets involve assumptions concerning comparable company
multiples, discount rates, growth projections and other assumptions of future business conditions. As the assumptions
employed to measure these assets and liabilities on a nonrecurring basis are based on management's judgment using