MasterCard 2013 Annual Report Download - page 16
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 16 of the 2013 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.12
• Other revenues: Other revenues consist of other payment-related products and services and primarily include
fees associated with consulting and research, fraud products and services, loyalty and rewards solutions,
program management services and a variety of other payment-related products and services.
• Rebates and incentives (contra-revenue): Rebates and incentives are provided to certain MasterCard customers
and are recorded as contra-revenue.
Pricing varies among our regions, and can be modified for our customers through customer-specific rebate and incentive
agreements, which provide customers with financial incentives and other support benefits to issue, accept, route,
prioritize and promote our branded products and other payment programs. These financial incentives may be based
on GDV or other performance-based criteria, such as issuance of new payment products, increased acceptance of our
products, launch of new programs or execution of marketing initiatives.
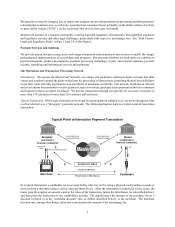
See “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations - Revenues” in Part II,
Item 7 for more detail about our revenue, GDV and processed transactions.
Intellectual Property
We own a number of valuable trademarks that are essential to our business, including MasterCard®, Maestro® and
Cirrus®, through one or more affiliates. We also own numerous other trademarks covering various brands, programs
and services offered by MasterCard to support our payment programs. Trademark and service mark registrations are
generally valid indefinitely as long as they are used and/or properly maintained. Through license agreements with our
customers, we authorize the use of our trademarks in connection with our customers' issuing and merchant acquiring
businesses. In addition, we own a number of patents and patent applications relating to payments solutions, transaction
processing, smart cards, contactless, mobile, electronic commerce, security systems and other matters, many of which
are important to our business operations. Patents are of varying duration depending on the jurisdiction and filing date.
Competition
We compete in the global payments industry against all forms of payment including:
• Paper-based payments (principally cash and checks);
• Card-based payments, including credit, charge, debit, ATM and prepaid products, and limited use products
such as private-label;
• Contactless, mobile and e-commerce payments; and
• Other electronic payments, including wire transfers, electronic benefits transfers, bill payments and automated
clearing house payments.
We face a number of competitors in the global payments industry:
• Cash and Check. Cash and check continue to represent the most widely-used forms of payment, constituting
approximately 85% of the world’s retail payment transactions. However, electronic forms of payment are
increasingly displacing paper forms of payment around the world, benefiting electronic payment brands.
• General Purpose Payment Networks. We compete worldwide with payment networks such as Visa, American
Express and Discover, among others. Among global networks, Visa has significantly greater volume than
we do. Outside of the United States, networks such as JCB in Japan and UnionPay in China have leading
positions in their domestic markets. In the case of UnionPay, it operates the sole domestic payment switch
in China. In addition, several governments are promoting, or considering promoting, local networks for
domestic processing.
• Debit. We compete with ATM and point-of-sale debit networks in various countries, such as Interlink®,
Plus® and Visa Electron® (owned by Visa Inc.), Star® (owned by First Data Corporation), NYCE® (owned
by FIS), and Pulse® (owned by Discover), in the United States; Interac in Canada; EFTPOS in Australia;