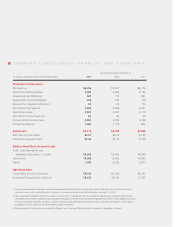
MasterCard 2013 Annual Report Download - page 10
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 10 of the 2013 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.6
Interchange Fees. Interchange fees represent a sharing of a portion of payments system costs among the issuers and
acquirers participating in our four-party payments system. They reflect the value merchants receive from accepting
our products and play a key role in balancing the costs consumers and merchants pay. We do not earn revenues from
interchange fees. Generally, interchange fees are collected from acquirers and paid to issuers to reimburse the issuers
for a portion of the costs incurred by them in providing services that benefit all participants in the system, including
acquirers and merchants. In some circumstances, such as cash withdrawal transactions, this situation is reversed and
interchange fees are paid by issuers to acquirers. We or financial institutions establish “default interchange fees” that
apply when there are no other established settlement terms in place between an issuer and an acquirer. We administer
the collection and remittance of interchange fees through the settlement process. Interchange fees can be a significant
component of the merchant discount rate, and therefore of the costs that merchants pay to accept electronic payments.
These fees are currently subject to regulatory, legislative and/or legal challenges in a number of jurisdictions. See “Risk
Factors-Legal and Regulatory Risks” in Part I, Item 1A.
Merchant Discount Rate. The merchant discount rate is established by the acquirer to cover its costs of both participating
in the four-party system and providing services rendered to merchants. The rate takes into consideration the amount
of the interchange fee which the acquirer generally pays to the issuer.
Additional Fees and Economic Considerations. Among the parties in a four-party system, various types of fees may
be charged to different constituents for various services. Acquirers may charge merchants processing and related fees
in addition to the merchant discount rate. Issuers may also charge cardholders fees for the transaction, including, for
example, fees for extending revolving credit. As described below, we charge issuers and acquirers fees for the transaction
processing and related services we provide.
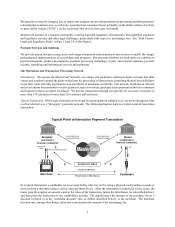
In a four-party payments system, the economics of a payment transaction relative to MasterCard vary widely depending
on such factors as whether the transaction is domestic (and, if it is domestic, the country in which it takes place) or
cross-border, whether it is a point-of-sale purchase transaction or cash withdrawal, and whether the transaction is
processed over our network or a third-party network or is handled solely by a financial institution that is both the
acquirer for the merchant and the issuer to the cardholder (an “on-us” transaction).
MasterCard Network Architecture. The MasterCard Network features a globally integrated structure that provides
scale for our issuer customers, enabling them to expand into regional and global markets. It features an intelligent
architecture that enables the network to adapt to the needs of each transaction by blending two distinct processing
structures-distributed (peer-to-peer) and centralized (hub-and-spoke):
• Transactions that require fast, reliable processing, such as those submitted using a contactless card or device
at a toll booth, can use the network's distributed processing structure, ensuring they are processed close to
where the transaction occurred.
• Transactions that require value-added processing, such as real-time access to transaction data for fraud scoring
or rewards at the point-of-sale, or customization of transaction data for unique consumer-spending controls,
use the network's centralized processing structure, ensuring advanced processing services are applied to the
transaction.
Our network’s architecture enables us to connect all parties regardless of whether the transaction is occurring at a
traditional physical location, at an ATM, on the internet or through a connected device. It has 24-hour a day availability
and world-class response time. The network incorporates multiple layers of protection, both for continuity purposes
and to address cyber-security challenges. We engage in multiple efforts to mitigate against such challenges, including
regularly testing our systems to address potential vulnerabilities.
Participation Standards. We establish, apply and enforce standards surrounding participation in the MasterCard
payments system. We grant licenses that provide issuers and acquirers that meet specified criteria with certain rights,
including access to the network and usage of cards and payment devices carrying our brands. As a condition of our
licenses, issuers and acquirers agree to comply with our standards surrounding participation and brand usage and
acceptance. We monitor areas of risk exposure and enforce our standards to combat fraudulent, illegal and brand-
damaging activity. Issuers and acquirers are also required to report instances of fraud to us in a timely manner so that
we can monitor trends and initiate action when appropriate.