MasterCard 2013 Annual Report Download - page 103
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 103 of the 2013 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
MASTERCARD INCORPORATED
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – (Continued)
99
Note 19. Settlement and Other Risk Management
MasterCard's rules guarantee the settlement of many of the MasterCard, Cirrus and Maestro branded transactions
between its issuers and acquirers ("settlement risk"). Settlement exposure is the outstanding settlement risk to customers
under MasterCard's rules due to the difference in timing between the payment transaction date and subsequent settlement.
While the term and amount of the guarantee are unlimited, the duration of settlement exposure is short term and typically
limited to a few days. Gross settlement exposure is estimated using the average daily card volume during the quarter
multiplied by the estimated number of days to settle. The Company has global risk management policies and procedures,
which include risk standards, to provide a framework for managing the Company's settlement risk. Customer-reported
transaction data and the transaction clearing data underlying the settlement exposure calculation may be revised in
subsequent reporting periods.
In the event that MasterCard effects a payment on behalf of a failed customer, MasterCard may seek an assignment of
the underlying receivables of the failed customer. Subject to approval by the Board of Directors, customers may be
charged for the amount of any settlement loss incurred during these ordinary course activities of the Company.
The Company's global risk management policies and procedures are aimed at managing the settlement exposure. These
risk management procedures include interaction with the bank regulators of countries in which it operates, requiring
customers to make adjustments to settlement processes, and requiring collateral from customers. MasterCard requires
certain customers that are not in compliance with the Company's risk standards in effect at the time of review to post
collateral, typically in the form of cash, letters of credit, or guarantees. This requirement is based on management's
review of the individual risk circumstances for each customer that is out of compliance. In addition to these amounts,
MasterCard holds collateral to cover variability and future growth in customer programs. The Company may also hold
collateral to pay merchants in the event of an acquirer failure. Although the Company is not contractually obligated
under its rules to effect such payments to merchants, the Company may elect to do so to protect brand integrity.
MasterCard monitors its credit risk portfolio on a regular basis and the adequacy of collateral on hand. Additionally,
from time to time, the Company reviews its risk management methodology and standards. As such, the amounts of
estimated settlement exposure are revised as necessary.
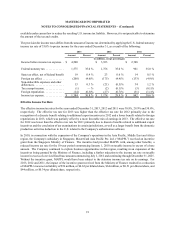
The Company's estimated settlement exposure from MasterCard, Cirrus and Maestro branded transactions was as
follows:
December 31,
2013 December 31,
2012
(in millions)
Gross settlement exposure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $ 40,657 $ 37,768
Collateral held for settlement exposure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (3,167)(3,775)
Net uncollateralized settlement exposure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $ 37,490 $ 33,993
General economic and political conditions in countries in which MasterCard operates affect the Company's settlement
risk. Many of the Company's financial institution customers have been directly and adversely impacted by political
instability and uncertain economic conditions. These conditions present increased risk that the Company may have to
perform under its settlement guarantee. This risk could increase if political, economic and financial market conditions
deteriorate further. The Company's global risk management policies and procedures are revised and enhanced from
time to time. Historically, the Company has experienced a low level of losses from financial institution failures.
MasterCard also provides guarantees to customers and certain other counterparties indemnifying them from losses
stemming from failures of third parties to perform duties. This includes guarantees of MasterCard-branded travelers
cheques issued, but not yet cashed of $503 million and $539 million at December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively, of
which $403 million and $434 million at December 31, 2013 and 2012 is mitigated by collateral arrangements. In
addition, the Company enters into business agreements in the ordinary course of business under which the Company
agrees to indemnify third parties against damages, losses and expenses incurred in connection with legal and other
proceedings arising from relationships or transactions with the Company. Certain indemnifications do not provide a