Lexmark 2008 Annual Report Download - page 105
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 105 of the 2008 Lexmark annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.consistent with the underlying asset and liability. Foreign exchange option contracts, as well as forward
contracts, may be used as fair value hedges in situations where derivative instruments, for which hedge
accounting has been discontinued, expose earnings to further change in exchange rates. Although, the
Company has historically used interest rate swaps to convert fixed rate financing activities to variable
rates, there were no interest rate swaps outstanding as of December 31, 2008.
Cash Flow Hedges: Cash flow hedges are hedges of forecasted transactions or of the variability of cash
flows to be received or paid related to a recognized asset or liability. During 2007 and 2006, Lexmark had
entered into foreign exchange options and forward exchange contracts, generally expiring within twelve
months, as hedges of anticipated purchases and sales that are denominated in foreign currencies. These
contracts were entered into to protect against the risk that the eventual cash flows resulting from such
transactions will be adversely affected by changes in exchange rates. However, the Company did not use
foreign exchange cash flow hedges during 2008. The Company enters into currency swap contracts to
hedge foreign currency risks that result from the transfer of various currencies within the Company. The
currency swap contracts entered into generally expire within one month.
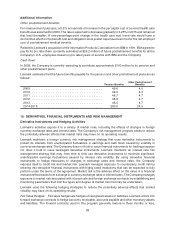
Accounting for Derivatives and Hedging Activities
All derivatives are recognized in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position at their fair value. Fair
values for Lexmark’s derivative financial instruments are based on pricing models or formulas using
current market data, or where applicable, quoted market prices. On the date the derivative contract is
entered into, the Company designates the derivative as either a fair value or cash flow hedge. Changes in
the fair value of a derivative that is highly effective as — and that is designated and qualifies as — a fair
value hedge, along with the loss or gain on the hedged asset or liability are recorded in current period
earnings in Cost of revenue on the Consolidated Statements of Earnings. Changes in the fair value of a
derivative that is highly effective as — and that is designated and qualifies as — a cash flow hedge are
recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive earnings (loss) on the Consolidated Statements of
Financial Position, until the underlying transactions occur, at which time the loss or gain on the
derivative is recorded in current period earnings in Cost of revenue on the Consolidated Statements of
Earnings. Derivatives qualifying as hedges are included in the same section of the Consolidated
Statements of Cash Flows as the underlying assets and liabilities being hedged.
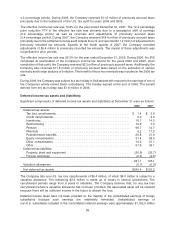
As of December 31, 2008, the Company had no derivative assets recorded in Prepaid expenses and other
current assets and $1.5 million of derivative liabilities recorded in Accrued liabilities on the Consolidated
Statements of Financial Position. As of December 31, 2007, the Company had derivative assets of
$0.7 million recorded in Prepaid expenses and other current assets and no derivative liabilities recorded in
Accrued liabilities on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position. As of December 31, 2008 and
2007, there were no deferred gains or losses on derivative instruments recorded in Accumulated other
comprehensive earnings (loss.)
Lexmark formally documents all relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as
its risk management objective and strategy for undertaking various hedge items. This process includes
linking all derivatives that are designated as fair value and cash flow to specific assets and liabilities on the
balance sheet. The Company also formally assesses, both at the hedge’s inception and on an ongoing
basis, whether the derivatives that are used in hedging transactions are highly effective in offsetting
changes in fair value or cash flows of hedged items. When it is determined that a derivative is not highly
effective as a hedge or that it has ceased to be a highly effective hedge, the Company discontinues hedge
accounting prospectively, as discussed below.
Lexmark discontinues hedge accounting prospectively when (1) it is determined that a derivative is no
longer effective in offsetting changes in the fair value or cash flows of a hedged item or (2) the derivative
expires or is sold, terminated or exercised. When hedge accounting is discontinued because it is
determined that the derivative no longer qualifies as an effective fair value hedge, the derivative will
continue to be carried on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Position at its fair value. In all other
situations in which hedge accounting is discontinued, the derivative will be carried at its fair value on the
99