HP 2012 Annual Report Download - page 121
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 121 of the 2012 HP annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
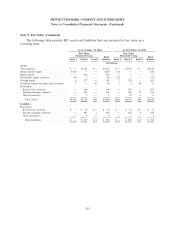
Note 9: Fair Value
HP determines fair value based on the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid
to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or
liability in an orderly transaction between market participants.
Valuation techniques used by HP are based upon observable and unobservable inputs. Observable
or market inputs reflect market data obtained from independent sources, while unobservable inputs
reflect HP’s assumptions about market participant assumptions based on the best information available.
Observable inputs are the preferred basis of valuation. These two types of inputs create the following
fair value hierarchy:
Level 1—Quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical instruments in active markets.
Level 2—Quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets, quoted prices for identical or
similar instruments in markets that are not active, and model-based valuation techniques for which all
significant assumptions are observable in the market or can be corroborated by observable market data
for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities.
Level 3—Prices or valuations that require management inputs that are both significant to the fair
value measurement and unobservable.
The following section describes the valuation methodologies HP uses to measure its financial assets
and liabilities at fair value.
Cash Equivalents and Investments: HP holds time deposits, money market funds, mutual funds,
other debt securities primarily consisting of corporate and foreign government notes and bonds, and
common stock and equivalents. Where applicable, HP uses quoted prices in active markets for identical
assets to determine fair value. If quoted prices in active markets for identical assets are not available to
determine fair value, HP uses quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities or inputs that are
observable either directly or indirectly. If quoted prices for identical or similar assets are not available,
HP uses internally developed valuation models, whose inputs include bid prices, and third-party
valuations utilizing underlying assets assumptions.
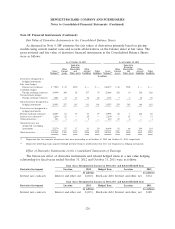
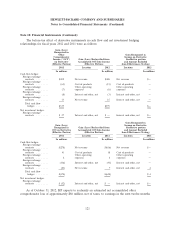
Derivative Instruments: As discussed in Note 10, HP mainly holds non-speculative forwards, swaps
and options to hedge certain foreign currency and interest rate exposures. When active market quotes
are not available, HP uses industry standard valuation models. Where applicable, these models project
future cash flows and discount the future amounts to a present value using market-based observable
inputs including interest rate curves, credit risk, foreign exchange rates, and forward and spot prices for
currencies. In certain cases, market-based observable inputs are not available and, in those cases, HP
uses management judgment to develop assumptions which are used to determine fair value.
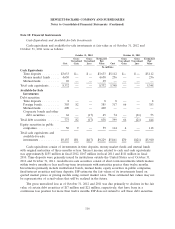
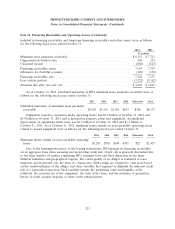
Short- and Long-Term Debt: The estimated fair value of publicly-traded debt is based on quoted
market prices for the identical liability when traded as an asset in an active market. For other debt for
which a quoted market price is not available, an expected present value method that uses rates
currently available to HP for debt with similar terms and remaining maturities is used to estimate fair
value. The portion of HP’s fixed-rate debt obligations that is hedged is reflected in the Consolidated
Balance Sheets as an amount equal to the debt’s carrying value, including a fair value adjustment
representing changes in the fair value of the hedged debt obligations arising from movements in
benchmark interest rates. The estimated fair value of HP’s short- and long-term debt approximated its
carrying value of $28.4 billion at October 31, 2012. The estimated fair value of HP’s short- and
113