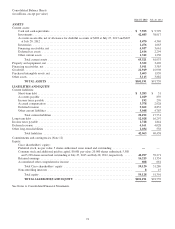
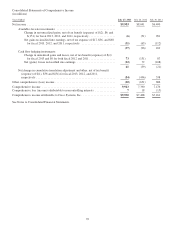
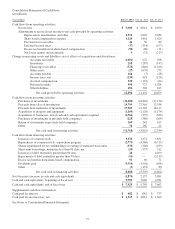
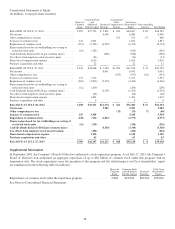
Cisco 2013 Annual Report Download - page 92
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 92 of the 2013 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
(q) Share-Based Compensation Expense The Company measures and recognizes the compensation expense for all share-based
awards made to employees and directors, including employee stock options, stock grants, stock units, and employee stock purchases
related to the Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“Employee Stock Purchase Rights”) based on estimated fair values. The fair value of
employee stock options is estimated on the date of grant using a lattice-binomial option-pricing model (“Lattice-Binomial Model”) or
the Black-Scholes model, and for employee stock purchase rights the Company estimates the fair value using the Black-Scholes
model. The fair value for time-based stock awards and stock awards that are contingent upon the achievement of financial
performance metrics is based on the grant date share price reduced by the present value of the expected dividend yield prior to
vesting. The fair value of market-based stock awards is estimated using an option-pricing model on the date of grant. Because share-
based compensation expense is based on awards ultimately expected to vest, it has been reduced for forfeitures.
(r) Software Development Costs Software development costs, including costs to develop software sold, leased, or otherwise
marketed, that are incurred subsequent to the establishment of technological feasibility are capitalized if significant. Costs
incurred during the application development stage for internal-use software are capitalized if significant. Capitalized software
development costs are amortized using the straight-line amortization method over the estimated useful life of the applicable
software. Such software development costs required to be capitalized have not been material to date.
(s) Income Taxes Income tax expense is based on pretax financial accounting income. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are
recognized for the expected tax consequences of temporary differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their
reported amounts. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount that will more likely than not
be realized.
The Company accounts for uncertainty in income taxes using a two-step approach to recognizing and measuring uncertain tax
positions. The first step is to evaluate the tax position for recognition by determining if the weight of available evidence
indicates that it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained on audit, including resolution of related appeals or
litigation processes, if any. The second step is to measure the tax benefit as the largest amount that is more than 50% likely of
being realized upon settlement. The Company classifies the liability for unrecognized tax benefits as current to the extent that
the Company anticipates payment (or receipt) of cash within one year. Interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions
are recognized in the provision for income taxes.
(t) Computation of Net Income per Share Basic net income per share is computed using the weighted-average number of
common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net income per share is computed using the weighted-average number
of common shares and dilutive potential common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted shares outstanding include the
dilutive effect of in-the-money options, unvested restricted stock, and restricted stock units. The dilutive effect of such equity
awards is calculated based on the average share price for each fiscal period using the treasury stock method. Under the treasury
stock method, the amount the employee must pay for exercising stock options, the amount of compensation cost for future
service that the Company has not yet recognized, and the amount of tax benefits that would be recorded in additional paid-in
capital when the award becomes deductible are collectively assumed to be used to repurchase shares.
(u) Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities The Company uses a qualitative approach in assessing the consolidation
requirement for variable interest entities. The approach focuses on identifying which enterprise has the power to direct the
activities that most significantly impact the variable interest entity’s economic performance and which enterprise has the
obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits from the variable interest entity. In the event that the Company is the
primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity, the assets, liabilities, and results of operations of the variable interest entity
will be included in the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
(v) Use of Estimates The preparation of financial statements and related disclosures in conformity with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the amounts reported in
the Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes. Estimates are used for the following, among others:
• Revenue recognition
• Allowances for accounts receivable, sales returns, and financing receivables
• Inventory valuation and liability for purchase commitments with contract manufacturers and suppliers
• Warranty costs
• Share-based compensation expense
• Fair value measurements and other-than-temporary impairments
• Goodwill and purchased intangible asset impairments
• Income taxes
• Loss contingencies
84