Cisco 2013 Annual Report Download - page 64
Download and view the complete annual report
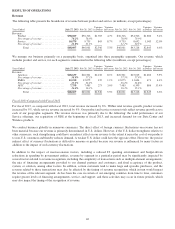
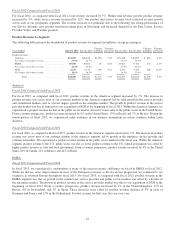
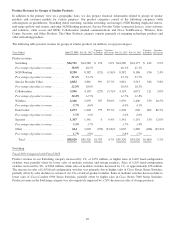
Please find page 64 of the 2013 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Factors That May Impact Revenue and Gross Margin
Product revenue may continue to be affected by factors, including global economic downturns and related market uncertainty,
that have resulted in cautious IT-related capital spending in our enterprise, service provider, public sector, and commercial
markets; changes in the geopolitical environment and global economic conditions; competition, including price-focused
competitors from Asia, especially from China; new product introductions; sales cycles and product implementation cycles;
changes in the mix of our customers between service provider and enterprise markets; changes in the mix of direct sales and
indirect sales; variations in sales channels; and final acceptance criteria of the product, system, or solution as specified by the
customer. Sales to the service provider market have been and may be in the future characterized by large and sporadic
purchases, especially relating to our router sales and sales of certain products within our Collaboration and Data Center
product categories. In addition, service provider customers typically have longer implementation cycles; require a broader
range of services, including network design services; and often have acceptance provisions that can lead to a delay in revenue
recognition. Certain of our customers in certain emerging countries also tend to make large and sporadic purchases, and the
revenue related to these transactions may similarly be affected by the timing of revenue recognition. As we focus on new
market opportunities, customers may require greater levels of financing arrangements, service, and support, especially in
certain emerging countries, which in turn may result in a delay in the timing of revenue recognition. To improve customer
satisfaction, we continue to focus on managing our manufacturing lead-time performance, which may result in corresponding
reductions in order backlog. A decline in backlog levels could result in more variability and less predictability in our quarter-
to-quarter revenue and operating results.
Product revenue may also be adversely affected by fluctuations in demand for our products, especially with respect to
telecommunications service providers and Internet businesses, whether or not driven by any slowdown in capital expenditures
in the service provider market; price and product competition in the communications and information technology industry;
introduction and market acceptance of new technologies and products; adoption of new networking standards; and financial
difficulties experienced by our customers. We may, from time to time, experience manufacturing issues that create a delay in
our suppliers’ ability to provide specific components, resulting in delayed shipments. To the extent that manufacturing issues
and any related component shortages result in delayed shipments in the future, and particularly in periods when we and our
suppliers are operating at higher levels of capacity, it is possible that revenue for a quarter could be adversely affected if such
matters are not remediated within the same quarter. For additional factors that may impact product revenue, see “Part I,
Item 1A. Risk Factors.”
Our distributors participate in various cooperative marketing and other programs. Increased sales to our distributors generally
result in greater difficulty in forecasting the mix of our products and, to a certain degree, the timing of orders from our
customers. We recognize revenue for sales to our distributors generally based on a sell-through method using information
provided by them, and we maintain estimated accruals and allowances for all cooperative marketing and other programs.
Product gross margin may be adversely affected in the future by changes in the mix of products sold, including periods of
increased growth of some of our lower margin products; introduction of new products, including products with price-
performance advantages, and new business models for our offerings such as XaaS; our ability to reduce production costs; entry
into new markets, including markets with different pricing structures and cost structures, as a result of internal development or
through acquisitions; changes in distribution channels; price competition, including competitors from Asia, especially those
from China; changes in geographic mix of our product revenue; the timing of revenue recognition and revenue deferrals; sales
discounts; increases in material or labor costs, including share-based compensation expense; excess inventory and
obsolescence charges; warranty costs; changes in shipment volume; loss of cost savings due to changes in component pricing;
effects of value engineering; inventory holding charges; and the extent to which we successfully execute on our strategy and
operating plans. Additionally, our manufacturing-related costs may be negatively impacted by constraints in our supply chain.
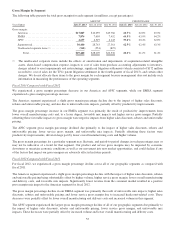
Service gross margin may be impacted by various factors such as the change in mix between technical support services and
advanced services; the timing of technical support service contract initiations and renewals; share-based compensation
expense; and the timing of our strategic investments in headcount and resources to support this business.
56