Cisco 2009 Annual Report Download - page 63
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 63 of the 2009 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
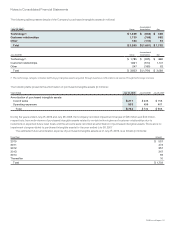
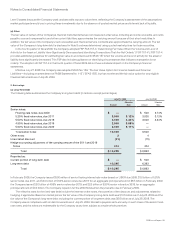
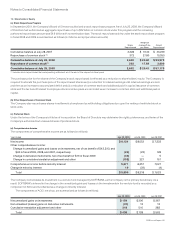
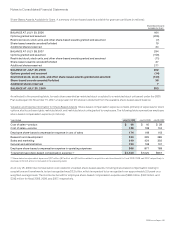
The effect of the Company’s cash flow hedging instruments on OCI and the Consolidated Statement of Operations for the year ended
July 25, 2009 is summarized as follows (in millions):
GAINS (LOSSES)
RECOGNIZED IN OCI
ON DERIVATIVES
(EFFECTIVE
PORTION)
GAINS (LOSSES) RECLASSIFIED FROM
AOCI INTO INCOME
(EFFECTIVE PORTION)
GAINS (LOSSES) RECOGNIZED
IN INCOME (INEFFECTIVE PORTION)(1)
Derivatives Designated as Cash Flow
Hedging Instruments Amount
Line Item in Statements
of Operations Amount
Line Item in Statements
of Operations Amount
Foreign currency derivatives $(116) Operating expenses $ (95) Other income (loss), net $ —
Cost of sales-service (13)
Interest rate derivatives (42)
Interest income (expense), net
—
Interest income (expense), net
(4)
Other derivatives (2) Operating expenses (2) Other income (loss), net —
Total $(160) $(110) $ (4)
(1) The Company did not exclude any component of the changes in fair value of the derivative instruments from the assessment of hedge effectiveness.
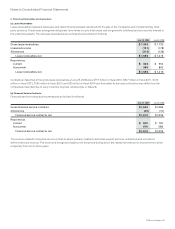
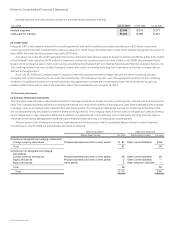
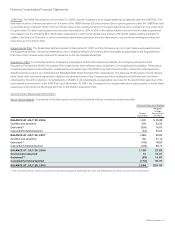
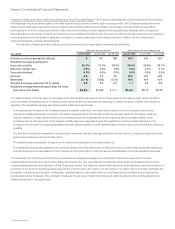
The effect on the Consolidated Statement of Operations for the year ended July 25, 2009 of derivative instruments designated as fair value
hedges is summarized as follows (in millions):
Derivatives Designated as Fair Value Hedging Instruments
Line Item in Statements
of Operations
Gains
(Losses)
Equity derivatives Other income (loss), net $ 97
Interest rate derivatives Other income (loss), net (7)
Total $90
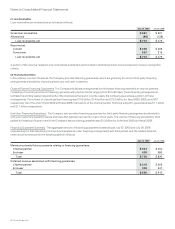
The effect on the Consolidated Statement of Operations for the year ended July 25, 2009 of derivative instruments not designated as
hedges is summarized as follows (in millions):
Derivatives not Designated as Hedging Instruments
Line Item in Statements
of Operations
Gains
(Losses)
Foreign currency derivatives Other income (loss), net $ 1
Equity derivatives Operating expenses (14)
Equity derivatives Other income (loss), net 11
Total $ (2)
As of July 25, 2009, the Company estimates that approximately $5 million of net derivative gains related to its cash flow hedges included in
AOCI will be reclassified into earnings within the next 12 months.
(b) Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
The Company conducts business globally in numerous currencies. As such, it is exposed to adverse movements in foreign currency
exchange rates. To limit the exposure related to foreign currency changes, the Company enters into foreign currency contracts. The
Company does not enter into such contracts for trading purposes.
The Company hedges foreign currency forecasted transactions related to certain operating expenses and service cost of sales with
currency options and forward contracts. These currency option and forward contracts, designated as cash flow hedges, generally have
maturities of less than 18 months. The Company assesses effectiveness based on changes in total fair value of the derivatives. The effective
portion of the derivative’s gain or loss is initially reported as a component of AOCI and subsequently reclassified into earnings when the
hedged exposure affects earnings. The ineffective portion, if any, of the gain or loss is reported in earnings immediately. The Company did
not discontinue any hedges during any of the periods presented because it was probable that the original forecasted transaction would not
occur.
2009 Annual Report 61