Cisco 2009 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 2009 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Share-Based Compensation Expense
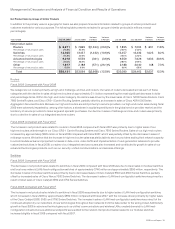
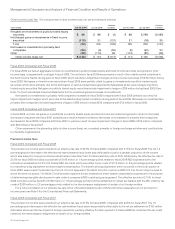
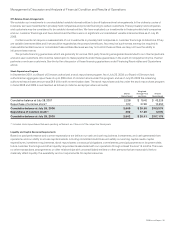
Employee share-based compensation expense was as follows (in millions):
Years Ended July 25, 2009 July 26, 2008 July 28, 2007
Cost of sales—product $46 $40 $39
Cost of sales—service 128 108 104
Employee share-based compensation expense in cost of sales 174 148 143
Research and development 333 295 289
Sales and marketing 440 434 392
General and administrative 193 148 107
Employee share-based compensation expense in operating expenses 966 877 788
Total employee share-based compensation expense(1) $ 1,140 $ 1,025 $ 931
(1) Share-based compensation expense related to acquisitions and investments of $91 million, $87 million and $34 million for fiscal 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, is
disclosed in Note 3 to the Consolidated Financial Statements and is not included in the preceding table.
Employee share-based compensation expense for fiscal 2009 increased compared with fiscal 2008 primarily due to a larger proportion of
share-based awards being subject to straight-line vesting, a shorter vesting period of four years for most share-based awards granted in
fiscal 2009, and an increase in the weighted-average estimated grant date fair value for each share-based award. The increase in
employee share-based compensation expense in fiscal 2008 compared with fiscal 2007 was primarily due to the higher weighted-average
estimated grant date fair value for each share-based award. See Note 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Amortization of Purchased Intangible Assets and In-Process Research and Development
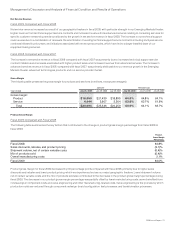
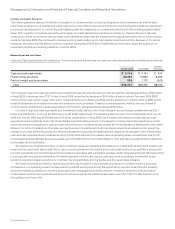
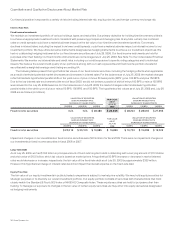
The following table presents the amortization of purchased intangible assets included in operating expenses and in-process R&D (in
millions):
Years Ended July 25, 2009 July 26, 2008 July 28, 2007
Amortization of purchased intangible assets included in operating expenses $ 533 $ 499 $ 407
In-process research and development 63 381
Total $ 596 $ 502 $ 488
For fiscal 2009, the increase in the amortization of purchased intangible assets included in operating expenses was primarily due to
impairment charges of $95 million in connection with write-downs of purchased intangible assets related to certain technologies and
customer relationships as a result of reductions in expected future cash flows from those technologies and relationships. This effect was
partially offset by lower amortization in fiscal 2009 from certain purchased intangible assets, primarily from the Scientific-Atlanta acquisition,
that became fully amortized during fiscal 2009. For additional information regarding purchased intangible assets, see Note 4 to the
Consolidated Financial Statements. The increase in the amortization of purchased intangible assets for fiscal 2008 compared with fiscal
2007 was primarily due to the additional amortization of purchased intangible assets related to acquisitions completed near the end of
fiscal 2007.
In-process R&D is expensed upon acquisition when technological feasibility has not been established and no future alternative uses
exist. The increase in in-process R&D for fiscal 2009 compared with fiscal 2008 was due to acquisitions completed in fiscal 2009. See Note
3 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding the acquisitions completed in fiscal 2009, 2008, and 2007,
and the associated in-process R&D recorded for those acquisitions.
Our methodology for allocating the purchase price for acquisitions to in-process R&D is determined through established valuation
techniques. The fair value of acquired purchased technology and patents, as well as technology under development, is typically
determined using the income approach, which discounts expected future cash flows to present value. The discount rates used in the
present value calculations are typically derived from a weighted-average cost of capital analysis and then adjusted to reflect risks inherent
in the development lifecycle as appropriate. We consider the pricing model for products related to these acquisitions to be standard within
the high-technology communications industry. However, we do not expect to achieve a material amount of expense reductions as a result
of integrating the acquired in-process technology. Therefore, the valuation assumptions do not include significant anticipated cost savings.
26 Cisco Systems, Inc.