Foot Locker 2014 Annual Report Download - page 80
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 80 of the 2014 Foot Locker annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
FOOT LOCKER, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
17. Income Taxes − (continued)
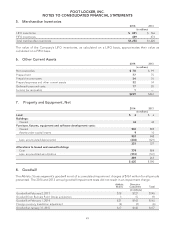
The following table summarizes the activity related to unrecognized tax benefits:
2014 2013 2012
(in millions)
Unrecognized tax benefits at beginning of year $48 $54 $ 65
Foreign currency translation adjustments (6) (4) 1
Increases related to current year tax positions 334
Increases related to prior period tax positions 143
Decreases related to prior period tax positions (1) (2) (3)
Settlements (1) (7) (15)
Lapse of statute of limitations (4) — (1)
Unrecognized tax benefits at end of year $40 $48 $ 54
It is reasonably possible that the liability associated with the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits will increase
or decrease within the next twelve months. These changes may be the result of foreign currency fluctuations,
ongoing audits or the expiration of statutes of limitations. Settlements could increase earnings in an amount
ranging from $0 to $5 million based on current estimates. Audit outcomes and the timing of audit settlements
are subject to significant uncertainty. Although management believes that adequate provision has been made
for such issues, the ultimate resolution could have an adverse effect on the earnings of the Company.
Conversely, if these issues are resolved favorably in the future, the related provision would be reduced,
generating a positive effect on earnings. Due to the uncertainty of amounts and in accordance with its
accounting policies, the Company has not recorded any potential impact of these settlements.
18. Financial Instruments and Risk Management
The Company operates internationally and utilizes certain derivative financial instruments to mitigate its foreign
currency exposures, primarily related to third-party and intercompany forecasted transactions. As a result of the
use of derivative instruments, the Company is exposed to the risk that counterparties will fail to meet their
contractual obligations. To mitigate this counterparty credit risk, the Company has a practice of entering into
contracts only with major financial institutions selected based upon their credit ratings and other financial
factors. The Company monitors the creditworthiness of counterparties throughout the duration of the derivative
instrument.
Additional information is contained within Note 19, Fair Value Measurements.
Derivative Holdings Designated as Hedges
For a derivative to qualify as a hedge at inception and throughout the hedged period, the Company formally
documents the nature of the hedged items and the relationships between the hedging instruments and the
hedged items, as well as its risk-management objectives, strategies for undertaking the various hedge
transactions, and the methods of assessing hedge effectiveness and ineffectiveness. In addition, for hedges of
forecasted transactions, the significant characteristics and expected terms of a forecasted transaction must be
specifically identified, and it must be probable that each forecasted transaction would occur. If it were deemed
probable that the forecasted transaction would not occur, the gain or loss on the derivative instrument would
be recognized in earnings immediately. No such gains or losses were recognized in earnings for any of the
periods presented. Derivative financial instruments qualifying for hedge accounting must maintain a specified
level of effectiveness between the hedging instrument and the item being hedged, both at inception and
throughout the hedged period, which management evaluates periodically.
The primary currencies to which the Company is exposed are the euro, British pound, Canadian dollar, and
Australian dollar. For the most part, merchandise inventories are purchased by each geographic area in their
respective local currency other than in the United Kingdom, which purchases its merchandise inventories using
the euro.
57