Volvo 2003 Annual Report Download - page 39
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 39 of the 2003 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
37
accordance with the principles set forth in the Recommendation of
the Swedish Financial Accounting Standards Council, RR 1:00,
Consolidated Financial Statements and Business Combinations.
All business combinations are accounted for in accordance with
the purchase method.
Companies that have been divested are included in the consolidat-
ed financial statements up to and including the date of divestment.
Companies acquired during the year are consolidated as of the date
of acquisition.
Joint ventures are preferably reported by use of the proportionate
method of consolidation. A few joint ventures are reported by use of
the equity method due to practical reasons.
Holdings in associated companies are reported in accordance
with the equity method. The Group’s share of reported income after
financial items in such companies, adjusted for minority interests, is
included in the consolidated income statement in Income from
investments in associated companies, reduced in appropriate cases
by amortization of goodwill. The Group’s share of reported taxes in
associated companies, is included in Group income tax expense.
For practical reasons, most of the associated companies are
included in the consolidated accounts with a certain time lag, nor-
mally one quarter. Dividends from associated companies are not
included in consolidated income. In the consolidated balance sheet,
the book value of shareholdings in associated companies is affected
by Volvo’s share of the company’s net income, reduced by the amort-
ization of goodwill and by the amount of dividends received.
Accounting for hedges
Loans and other financial instruments used to hedge an underlying
position are reported as hedges. In order to apply hedge accounting,
the following criteria must be met: the position being hedged is iden-
tified and exposed to exchange-rate or interest-rate movements, the
purpose of the loan/ instrument is to serve as a hedge and the hedg-
ing effectively protects the underlying position against changes in
the market rates. Financial instruments used for the purpose of
hedging future currency flows are accounted for as hedges if the
currency flows are considered probable to occur.
Foreign currencies
In preparing the consolidated financial statements, all items in the
income statements of foreign subsidiaries and joint ventures (except
subsidiaries in highly inflationary economies) are translated to Swedish
kronor at the average exchange rates during the year (average rate).
All balance sheet items except net income are translated at ex-
change rates at the respective year-ends (year-end rate). The differ-
ences in consolidated shareholders’ equity arising as a result of vari-
ations between year-end exchange rates are charged or credited
directly to shareholders’ equity and classified as restricted or un-
restricted reserves. The difference arising in the consolidated bal-
ance sheet as a result of the translation of net income, in the income
statements, in foreign subsidiaries’ to Swedish kronor at average
rates, and in the balance sheets at year-end rate, is charged or
credited to unrestricted reserves. Movements in exchange rates
change the book value of foreign associated companies. This differ-
ence affects restricted reserves directly.
When foreign subsidiaries, joint ventures and associated compa-
nies are divested, the accumulated translation difference is reported
as a realized gain/ loss and, accordingly, affects the capital gain.
Financial statements of subsidiaries operating in highly inflationary
economies are translated to Swedish kronor using the monetary
method. Monetary items in the balance sheet are translated at year-
end rates and nonmonetary balance sheet items and corresponding
income statement items are translated at rates in effect at the time
of acquisition (historical rates). Other income statement items are
translated at average rates. Translation differences are credited to, or
charged against, income in the year in which they arise.
In the individual Group companies as well as in the consolidated
accounts, receivables and liabilities in foreign currency are valued at
period-end exchange rates.
Gains and losses pertaining to hedges are reported at the same
time as gains and losses of the items hedged. Received premiums or
payments for currency options, which hedge currency flows in busi-
ness transactions, are reported as income/ expense during the con-
tract period.
Gains/ losses on outstanding currency futures at year-end, which
were entered into to hedge future commercial currency flows, are
reported at the same time as the commercial flow is realized. For
other currency futures that do not fullfil the criteria for hedge
accounting a full market valuation is made on a portfolio basis and
are credited to, or charged against, income.
In valuing financial assets and liabilities whose original currency
denomination has been changed as a result of currency swap con-
tracts, the loan amount is accounted for translated to Swedish kro-
nor at the period-end exchange rate. Unrealized exchange rate gains
relating to swap contracts are reported among short-term receiv-
ables and unrealized exchange rate losses relating to swap contracts
are reported among current liabilities.
Exchange rate differences on loans and other financial instru-
ments in foreign currency, which are used to hedge net assets in for-
eign subsidiaries and associated companies, are offset against trans-
lation differences in the shareholders’ equity of the respective com-
panies.
Exchange rate gains and losses on payments during the year and
on the valuation of assets and liabilities in foreign currencies at year-
end are credited to, or charged against, income in the year they arise.
The more important exchange rates employed are shown above.
Other financial instruments
Interest-rate contracts and forward exchange rate contracts are used
to change the underlying financial asset and debt structure and are
reported as hedges against such assets and debts.
Interest-rate contracts used as part of the management of the
Group’s short-term investments are valued together with these
investments in accordance with the portfolio method. Provisions are
made for unrealized losses in excess of the unrealized gains within
the portfolio.
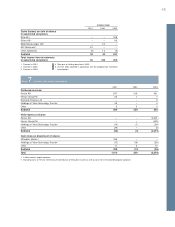
Exchange rates Average rate Year-end rate
Country Currency 2001 2002 2003 2001 2002 2003
Denmark DKK 1.2403 1.2326 1.2281 1.2670 1.2386 1.2226
Japan JPY 0.0850 0.0779 0.0697 0.0813 0.0740 0.0681
Norway NOK 1.1485 1.2205 1.1418 1.1840 1.2605 1.0815
Great Britain GBP 14.8763 14.5816 13.2023 15.4800 14.1538 12.9188
United States USD 10.3272 9.7287 8.0778 10.6700 8.8263 7.2763
Canada CAD 6.6721 6.1965 5.7688 6.6923 5.6335 5.5610
Euro EUR 9.2434 9.1596 9.1258 9.4240 9.2018 9.1033