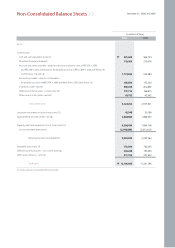
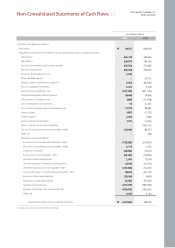
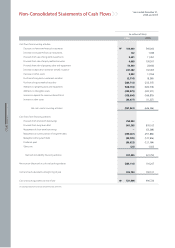
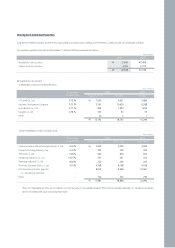
Kia 2006 Annual Report Download - page 63
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 63 of the 2006 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
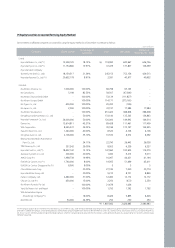
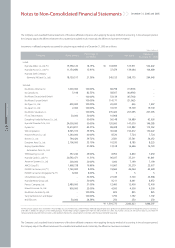
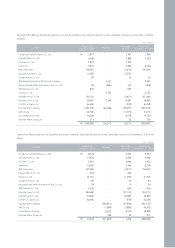
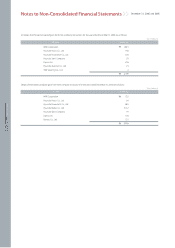
(q) Provision, Contingent Assets and Contingent Liabilities
Provisions are recognized when all of the following are met: (1) an entity has a present obligation as a result of a past event, (2) it is probable that an outflow of
resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation, and (3) a reliable estimate can be made of the amount of the obligation. Where
the effect of the time value of money is material, a provision is recorded at the present value of the expenditures expected to be required to settle the obligation.
Where the expenditure required to settle a provision is expected to be reimbursed by another party, the reimbursement is recognized as a separate asset when,
and only when, it is virtually certain that reimbursement will be received if the Company settles the obligation. The expense relating to a provision is presented net
of the amount recognized for a reimbursement.
The Company generally provides a warranty to the ultimate consumer for each product sold and accrues warranty expense at the time of sale based on actual
claims history. Also, the Company accrues potential expenses, which may occur due to product liability suit and voluntary recall campaign pending as of the
balance sheet date. Additionally, the Company recognizes accrued liabilities of the provision for the projected costs for dismantling and recycling vehicles that the
Company sold in the European Union region to comply with a European Parliament directive regarding End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV), in which manufacturers are
financially responsible for a portion of the cost of dismantling and recycling of the vehicles placed in service. If the effect of the time value of money is material, the
provision is valued at present value of the expenditures expected to be required to settle the obligation.
(r) Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue from the sale of goods when the goods are delivered. Revenue from other than the sale of goods is recognized when the
Company’s revenue-earning activities have been substantially completed, the amount of revenue can be measured reliably, and it is probable that the economic
benefits associated with the transaction will flow to the Company.
Long-term installment sales are recognized at the time of shipment of motor vehicles and parts when the significant risks and rewards of ownership of the goods
have been transferred to buyer. The interest income arising from long-term installment sales contracts is recognized using the level yielding method.
(s) Income Taxes
Deferred tax is provided using the asset and liability method, providing for temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial
reporting purposes and the amounts used for tax purposes. The amount of deferred tax provided is based on the expected manner of realization or settlement of
the carrying amount of assets and liabilities, using tax rates enacted or substantially enacted at the balance sheet date.
A deferred tax asset is recognized only to the extent that it is probable that future taxable income will be available against which the unused tax losses and credits
can be utilized. Deferred tax assets are reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that the related tax benefit will be realized.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are classified as current or non-current based on the classification of the related asset or liability for financial reporting or the
expected reversal date of the temporary difference for those with no related asset or liability such as loss carryforwards and tax credit carryforwards. The deferred
tax amounts are presented as a net current asset or liability and a net non-current asset or liability.
Deferred taxes are recognized on the temporary differences related to unrealized gains and losses on investment securities that are reported as a separate
component of capital adjustments.
(t) Earnings Per Share
Basic earnings per share are calculated by dividing net income by the weighed-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during each period.
Diluted earnings per share is determined in the same manner as basic earnings per share except that the number of shares is increased and earnings is decreased
to assume exercise of potentially dilutive stock options, unless the effect of such increase would be anti-dilutive.
(u) Use of Estimates
The preparation of non-consolidated financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the Republic of Korea requires