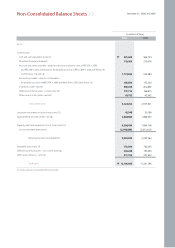
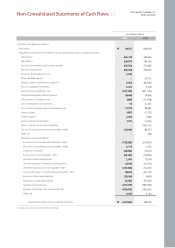
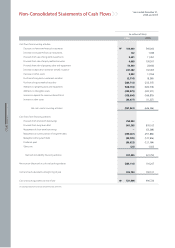
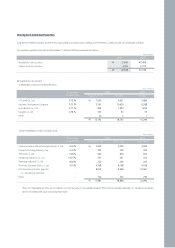
Kia 2006 Annual Report Download - page 61
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 61 of the 2006 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
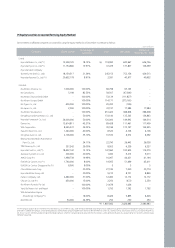
Assets and liabilities of foreign-based companies accounted for using the equity method are translated at current rate of exchange at the balance sheet date while
profit and loss items in the statement of income are translated at average rate and capital account at historical rate. The translation gains and losses arising from
collective translation of the foreign currency financial statements of foreign-based companies are offset and the balance is accumulated as capital adjustment.
Under the equity method of accounting, unrealized gains and losses on transactions with an investee are eliminated to the extent of the investor’s interest in the
investee. However, unrealized gains and losses from a down-stream transaction with a subsidiary are eliminated entirely.
Investments in affiliated companies are reduced when dividends are declared by shareholders’ meeting of the respective affiliated companies.
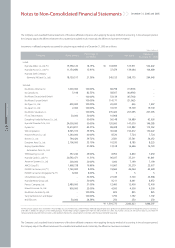
(i) Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost, except in the case of revaluation made in accordance with the old Asset Revaluation Law. However, assets
acquired through exchange, investment in kind or donation are recorded at their fair value upon acquisition.
Significant additions or improvements extending useful lives of assets are capitalized. However, normal maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as
incurred.
Depreciation is computed by the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets as follows:
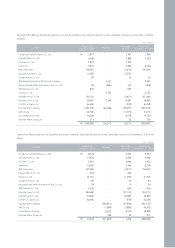
The Company recognizes interest costs and other financial charges on borrowings associated with the production, acquisition, construction of property, plant and
equipment as an expense in the period in which they are incurred.
The Company reviews the property, plant and equipment for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an
asset may not be recoverable. An impairment loss would be recognized when the expected estimated undiscounted future net cash flows from the use of the
asset and its eventual disposal are less than its carrying amount.
(j) Intangible Assets
Intangible assets are stated at cost less accumulated amortization, as described below:
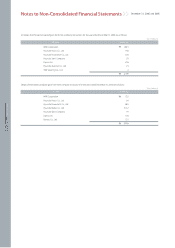
(i) Research and Development Costs
To assess whether an internally generated intangible asset meets the recognition criteria, the Company classifies the generation process into a research phase
and a development phase. All costs incurred during the research phase shall be expensed as incurred. Costs incurred during the development phase shall be
recognized as assets only if they satisfy all criteria for recognition. An intangible asset shall be recognized only if (1) it is probable that future economic benefits
that are attributable to the asset will flow into the entity and (2) the cost of the asset can be measured reliably. If the costs incurred fail to satisfy all of these
criteria, they shall be recorded as periodic expenses as incurred. Development cost is capitalized and amortized on a straight-line basis over the expected
periods to be benefited, generally three years. The expenditure capitalized includes the cost of materials, direct labor and an appropriate proportion of
overheads.
(ii) Other Intangible Assets
Other intangible assets, which consist of industrial property rights and right of utilization, are stated at cost less accumulated amortization and impairment
losses. Such intangible assets are amortized using the straight-line method over a reasonable period, generally five or ten years, based on the nature of the
asset.
Useful lives (years)
Buildings and structures 20-40
Machinery and equipment 15
Dies, molds and tools 5
Vehicles 5
Other equipment 5