Kia 2006 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 59 of the 2006 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
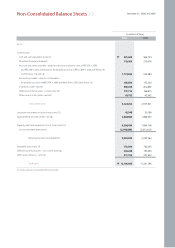
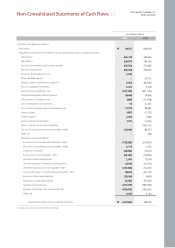
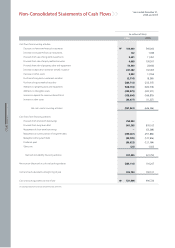
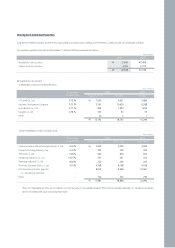
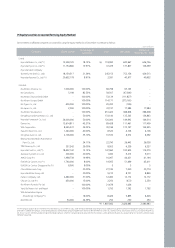
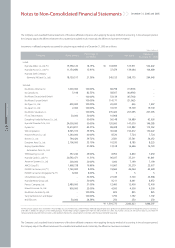
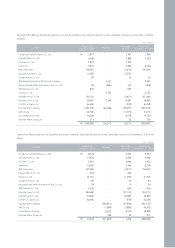
December 31, 2006 and 2005
Notes to Non-Consolidated Financial Statements
(1) Summary of Significant Accounting Policies and Basis of Presenting Financial Statements
(a) Organization and Description of the Business
Kia Motors Corporation (the”Company”), one of the leading motor vehicle manufacturers in Korea, was established on December 1944 under the laws of the
Republic of Korea to manufacture and sell a range of passenger cars, recreational vehicles and other commercial vehicles in the domestic and international markets.
The Company owns and operates three principal automobile production bases: the Sohari factory, the Hwasung factory and the Kwangju factory.
The shares of the Company have been listed on the Korea Exchange since 1973. As of December 31, 2006, the Company’s largest shareholder is Hyundai Motor
Company, which holds 38.7 percent of the Company’s stock.
Major overseas subsidiaries for international sales are Kia Motors America, Inc. (KMA) in the United States, Kia Canada, Inc. (KCI) in Canada, Kia Motors Deutschland
GmbH (KMD) and Kia Motors Europe GmbH (KME) in Germany. Also, the Company established an overseas assembly subsidiary in Zilina, Slovak Republic on
February 26, 2004 to establish a production capacity in Europe. The construction of the plant in Zilina was completed and the production started from the end of
2006.
(b) Basis of Presenting Financial Statements
The Company maintains its accounting records in Korean Won and prepares statutory non-consolidated financial statements in the Korean language in conformity
with accounting principles generally accepted in the Republic of Korea. Certain accounting principles applied by the Company that conform with financial
accounting standards and accounting principles in the Republic of Korea may not conform with generally accepted accounting principles in other countries.
Accordingly, these financial statements are intended solely for use by only those who are informed about Korean accounting principles and practices. The
accompanying non-consolidated financial statements have been condensed, restructured and translated into English from the Korean language non-consolidated
financial statements.
Certain information included in the Korean language non-consolidated financial statements, but not required for a fair presentation of the Company’s financial
position, results of operations or cash flows, is not presented in the accompanying non-consolidated financial statements.
The accompanying non-consolidated financial statements include only the accounts of the Company, but do not consolidate the accounts of any of its subsidiaries.
Instead, these subsidiaries are accounted for under the equity method of accounting (see note 7).
Effective January 1, 2006, the Company adopted Statements of Korea Accounting Standards No. 19, Leases, and No. 20, Related Party Disclosures. The adoption of
these standards did not have a significant impact on accompanying non-consolidated financial statements. As allowed by these standards, prior year balances
have not been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
(c) Cash Equivalents
The Company considers short-term financial instruments with maturities of three months or less at the acquisition date to be cash equivalents.
(d) Financial Instruments
Short-term financial instruments are instruments handled by financial institutions which are held for short-term cash management purposes, maturing within one
year. Such investments may include time deposits, installment savings deposits and restricted bank deposits.
(e) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
The allowance for doubtful accounts is estimated based on an analysis of individual accounts and past experience of collection. However, when principals of trade
accounts and notes receivable, interest rate or repayment period are changed unfavorably for the creditor by a court imposition, such as on commencement of
reorganization, or by mutual agreements and the difference between nominal value and present value is material, the difference is recognized as bad debt
expense.