IBM 2001 Annual Report Download - page 80
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 80 of the 2001 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
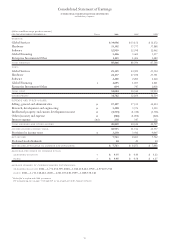
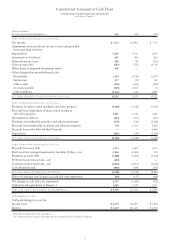
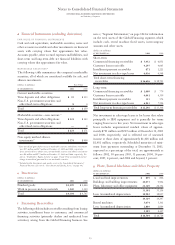
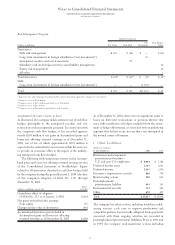
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION
and Subsidiary Companies
78
accounting does not apply under SFAS No. 133 or is not
applied by the company. In these cases, there generally exists
a natural hedging relationship in which changes in fair value
of the derivative, which are recognized currently in net
income, act as an economic offset to changes in the fair value
of the underlying hedged item(s).
Changes in the value of a derivative that is designated as a
fair value hedge, along with offsetting changes in fair value of
the underlying hedged exposure, are recorded in earnings each
period. For hedges of interest rate risk, the fair value adjust-
ments are recorded as adjustments to Interest expense and
Cost of Financing in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
For hedges of currency risk associated with recorded assets
or liabilities, derivative fair value adjustments generally are
recognized in Other income and expense in the Consolidated
Statement of Earnings. Changes in the value of a derivative
that is designated as a cash flow hedge are recorded in the
Accumulated gains and losses not affecting retained earnings, a
component of Stockholders’ equity. When net income is
affected by the variability of the underlying cash flow, the
applicable amount of the gain or loss from the derivative that
is deferred in Stockholders’ equity is released to net income
and reported in Interest expense, Cost, SG&A expense or
Other income and expense in the Consolidated Statement of
Earnings based on the nature of the underlying cash flow
hedged. Effectiveness for net investment hedging derivatives is
measured on a spot to spot basis. The effective portion of
changes in the fair value of derivatives and other non derivative
risk management instruments designated as net investment
hedges are recorded as foreign currency translation adjust-
ments in the Accumulated gains and losses not affecting
retained earnings section of Stockholders’ equity. Changes
in the fair value of the portion of a net investment hedging
derivative excluded from the effectiveness assessment are
recorded in Interest expense.
When the underlying hedged item ceases to exist, all
changes in the fair value of the instrument are included in
net income each period until the instrument matures. When
the underlying transaction ceases to exist, a hedged asset or
liability is no longer adjusted for changes in its fair value.
Derivatives that are not designated as hedges, as well as
changes in the value of derivatives that do not offset the
underlying hedged item throughout the designated hedge
period (collectively, “ineffectiveness”), are recorded in net
income each period and generally are reported in Other
income and expense. Refer to note k, “Derivatives and
Hedging Transactions,” on pages 85 through 87 for a
description of the major risk management programs and
classes of financial instruments used by the company.
FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
In determining fair value of its financial instruments, the com-
pany uses a variety of methods and assumptions that are based
on market conditions and risks existing at each balance sheet
date. For the majority of financial instruments including most
derivatives, long-term investments and long-term debt, stan-
dard market conventions and techniques such as discounted
cash flow analysis, option pricing models, replacement cost
and termination cost are used to determine fair value. Dealer
quotes are used for the remaining financial instruments. All
methods of assessing fair value result in a general approxima-
tion of value, and such value may never actually be realized.
CASH EQUIVALENTS
All highly liquid investments with a maturity of three
months or less at date of purchase are carried at fair value
and considered to be cash equivalents.
MARKETABLE SECURITIES
Marketable securities included in Current assets represent
securities with a maturity of less than one year. The com-
pany also has Marketable securities, including non equity
method alliance investments, with a maturity of more than
one year. These non current investments are included in
Investments and sundry assets. The company’s Marketable
securities, including certain non equity method alliance
investments, are considered available for sale and are
reported at fair value with changes in unrealized gains and
losses, net of applicable taxes, recorded in Accumulated
gains and losses not affecting retained earnings within
Stockholders’ equity. Realized gains and losses are calculated
based on the specific identification method. Other than tem-
porary declines in market value from original cost are
charged to Other income and expense in the period in which
the loss occurs. In determining whether an other than tempo-
rary decline in the market value has occurred, the company
considers the duration that and extent to which market value
is below original cost. Realized gains and losses and other
than temporary declines in market value from original cost
are included in Other income and expense in the
Consolidated Statement of Earnings. All other investment
securities not described above or in the “Principles of
Consolidation” on page 75, primarily non-publicly traded
equity securities, are accounted for using the cost method.
INVENTORIES
Raw materials, work in process and finished goods are stated
at the lower of average cost or net realizable value.