Holiday Inn 2008 Annual Report Download - page 58
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 58 of the 2008 Holiday Inn annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.56 IHG Annual Report and Financial Statements 2008
General information
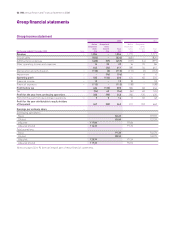
The consolidated financial statements of InterContinental Hotels
Group PLC (the Group or IHG) for the year ended 31 December 2008
were authorised for issue in accordance with a resolution of the
Directors on 16 February 2009. InterContinental Hotels Group PLC
(the Company) is incorporated in Great Britain and registered in
England and Wales.
Summary of significant accounting policies
Basis of preparation
The consolidated financial statements of IHG have been prepared
in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards
(IFRS) as adopted by the European Union and as applied in
accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act 1985.
The Group early adopted International Financial Reporting
Interpretations Committee Interpretation 14 ‘IAS 19 – The Limit
on a Defined Benefit Asset, Minimum Funding Requirements and
their Interaction’ (IFRIC 14) at 31 December 2007. IFRIC 14 provides
guidance on assessing the limit in International Accounting
Standard 19 ‘Employee Benefits’ (IAS 19) on the amount of the
surplus that can be recognised as an asset. The 31 December 2007
balance sheet has subsequently been restated to show the
retirement benefit assets net of tax of $17m previously recorded
within deferred tax payable. There have been corresponding
changes to the actuarial gains and related tax reported in the
restated Group statement of recognised income and expense
for the year ended 31 December 2007. There is no change to
previously reported net assets or income.
Other new accounting standards and interpretations issued by
the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and the
International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee
(IFRIC), becoming effective during the year, have not had a
material impact on the Group’s financial statements.
Change in presentational currency
The consolidated financial statements are presented in US dollars
following a management decision to change the reporting currency
from sterling during the year. The change has been made to reflect
the profile of the Group’s revenue and operating profit which
are now primarily generated in US dollars or US dollar-linked
currencies. All comparative information has been restated into
US dollars and values are rounded to the nearest million ($m)
except where otherwise indicated.
The currency translation reserve was set to nil at 1 January 2004
on transition to IFRS and this reserve has been re-presented on
the basis that the Group has reported in US dollars since this date.
Equity share capital, the capital redemption reserve and shares
held by employee share trusts are translated into US dollars at
the rates of exchange on the balance sheet date; the resultant
exchange differences are recorded in other reserves.
The functional currency of the parent company remains sterling
since this is a non-trading holding company located in the United
Kingdom that has sterling denominated share capital and whose
primary activity is the receipt and payment of interest on sterling
denominated inter-company balances.
Basis of consolidation
The Group financial statements comprise the financial statements
of the parent company and entities controlled by the Company.
All intra-group balances and transactions have been eliminated.
The results of those businesses acquired or disposed of are
consolidated for the period during which they were under the
Group’s control.
Foreign currencies
Transactions in foreign currencies are translated to the
functional currency at the exchange rates ruling on the dates
of the transactions. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated
in foreign currencies are retranslated to the functional currency
at the relevant rates of exchange ruling at the balance sheet
date. All foreign exchange differences arising on translation are
recognised in the income statement except on foreign currency
borrowings that provide a hedge against a net investment in
a foreign operation. These are taken directly to the currency
translation reserve until the disposal of the net investment, at
which time they are recycled against the gain or loss on disposal.
The assets and liabilities of foreign operations, including goodwill,
are translated into US dollars at the relevant rates of exchange
ruling at the balance sheet date. The revenues and expenses of
foreign operations are translated into US dollars at average rates
of exchange for the period. The exchange differences arising on
the retranslation are taken directly to the currency translation
reserve. On disposal of a foreign operation, the cumulative
amount recognised in the currency translation reserve relating
to that particular foreign operation is recycled against the gain
or loss on disposal.
Derivative financial instruments and hedging
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments are accounted
for in line with the nature of the hedging arrangement. The
Group’s detailed accounting policies with respect to hedging
instruments are set out in note 21. Documentation outlining the
measurement and effectiveness of the hedging arrangement is
maintained throughout the life of the hedge relationship. Any
ineffective element of a hedge arrangement is recognised in
financial income or expense.
Interest arising from currency swap agreements is taken to
financial income or expense on a gross basis over the term of
the relevant agreements. Interest arising from other currency
derivatives and interest rate swaps is taken to financial income
or expense on a net basis over the term of the agreement.
Foreign exchange gains and losses on currency derivatives are
recognised in financial income and expense unless they form
part of effective hedge relationships.
The fair value of derivatives is calculated by discounting the
expected future cash flows at prevailing interest rates.
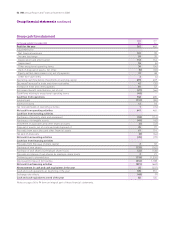
Accounting policies