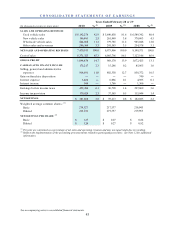
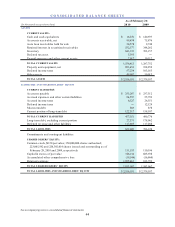
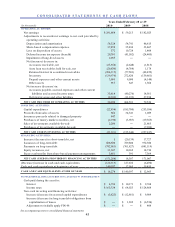
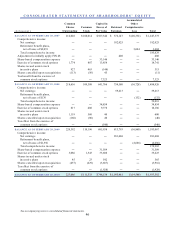
CarMax 2010 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 59 of the 2010 CarMax annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.49
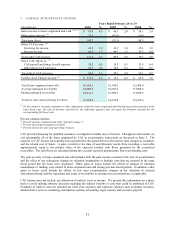
We sell extended service plans and guaranteed asset protection (“GAP”) on behalf of unrelated third parties. The
service plans have terms of coverage ranging from 12 to 72 months, while GAP covers the customer for the entire
term of their finance contract. Because we are not the primary obligor under these products, we recognize
commission revenue at the time of sale, net of a reserve for estimated customer returns. The reserve for returns is
based on historical experience and trends.
We collect sales taxes and other taxes from customers on behalf of governmental authorities at the time of sale.
These taxes are accounted for on a net basis and are not included in net sales and operating revenues or cost of sales.
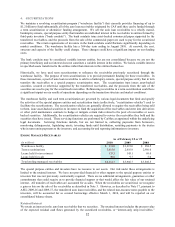
(L) Cost of Sales
Cost of sales includes the cost to acquire vehicles and the reconditioning and transportation costs associated with
preparing the vehicles for resale. It also includes payroll, fringe benefits and parts and repair costs associated with
reconditioning and vehicle repair services.
(M) Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative (“SG&A”) expenses primarily include rent and occupancy costs; payroll
expenses, other than payroll related to reconditioning and vehicle repair services; fringe benefits; advertising; and
other general expenses.
(N) Advertising Expenses
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred. Advertising expenses are included in SG&A expenses. See Note 15(D)
for additional information.
(O) Store Opening Expenses
Costs related to store openings, including preopening costs, are expensed as incurred and are included in SG&A
expenses.
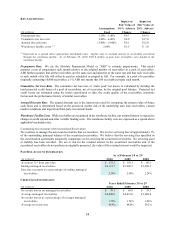
(P) Share-Based Compensation
Share-based compensation represents the cost related to share-based awards granted to employees and non-
employee directors. We measure share-based compensation cost at the grant date, based on the estimated fair value
of the award, and we recognize the cost on a straight-line basis (net of estimated forfeitures) over the grantee’s
requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period of the award. We estimate the fair value of stock
options using a binomial valuation model. Prior to fiscal 2009, we used the Black-Scholes valuation model for the
directors’ plan. Key assumptions used in estimating the fair value of options are dividend yield, expected volatility,
risk-free interest rate and expected term. The fair value of restricted stock is based on the weighted average market
value on the date of the grant. The fair value of stock-settled restricted stock units is determined using a Monte-
Carlo simulation based on the expected market price of our common stock on the vesting date and the expected
number of converted common shares. Cash-settled restricted stock units are liability awards with fair value
measurement based on the market price of CarMax common stock at the end of each reporting period. Share-based
compensation expense is recorded in either cost of sales, CAF income or SG&A expenses based on the recipients’
respective function.
We record deferred tax assets for awards that result in deductions on our income tax returns, based on the amount of
compensation expense recognized and the statutory tax rate in the jurisdiction in which we will receive a deduction.
Differences between the deferred tax assets recognized for financial reporting purposes and the actual tax deduction
reported on the income tax return are recorded in capital in excess of par value (if the tax deduction exceeds the
deferred tax asset) or in the consolidated statements of earnings (if the deferred tax asset exceeds the tax deduction
and no capital in excess of par value exists from previous awards).
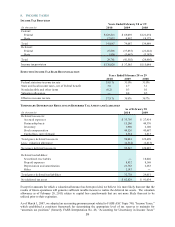
(Q) Financial Derivatives
In connection with certain securitization activities, we enter into derivative agreements to manage our exposure to
interest rates, to more closely match funding costs to the use of funding and to limit the risk for investors in our
warehouse facility. We recognize the derivatives at fair value as either current assets or current liabilities. Where
applicable, such contracts covered by master netting agreements are reported net. Gross positive fair values are
netted with gross negative fair values by counterparty pursuant to a valid master netting agreement. Changes in fair
value of derivatives are included in earnings as a component of CAF income.