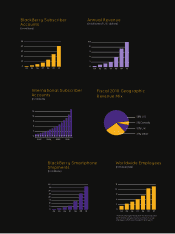
Blackberry 2010 Annual Report Download - page 16
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 16 of the 2010 Blackberry annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue when it is realized or realizable and earned. The Company considers
revenue realized or realizable and earned when it has persuasive evidence of an arrangement, the product
has been delivered or the services have been provided to the customer, the sales price is fixed or determinable
and collectability is reasonably assured. In addition to this general policy, the following paragraphs describe
the specific revenue recognition policies for each major category of revenue.
Devices
Revenue from the sale of BlackBerry devices is recognized when title is transferred to the customer and all
significant contractual obligations that affect the customer’s final acceptance have been fulfilled. For hardware
products for which the software is deemed not to be incidental, the Company recognizes revenue in
accordance with industry-specific software revenue recognition guidance. In addition, provisions are made at
the time of sale for warranties and royalties. For additional information on warranties and royalties, see below.
Service
Revenue is recognized rateably on a monthly basis when the service is provided. In instances where the
Company bills the customer prior to performing the service, the prebilling is recorded as deferred revenue. See
“Sources of Revenue” for more information on the calculation of the number of subscriber accounts.
Software
Revenue from licensed software is recognized at the inception of the license term and in accordance with
industry-specific software revenue recognition guidance.When the fair value of a delivered element has not
been established, the Company uses the residual method to recognize revenue if the fair value of undelivered
elements is determinable.Revenue from software maintenance, unspecified upgrades and T-Support contracts
is recognized over the period that such items are delivered or that services are provided.
Other
Revenue from the sale of accessories is recognized when title is transferred to the customer and all significant
contractual obligations that affect the customer’s final acceptance have been fulfilled. Revenue for non-
recurring engineering contracts is recognized as specific contract milestones are met. The attainment of
milestones approximates actual performance. Revenue from repair and maintenance programs is recognized
when the service is delivered which is when the title is transferred to the customer and all significant
contractual obligations that affect the customer’s final acceptance have been fulfilled.
Multiple-Element Arrangements
The Company enters into transactions that represent multiple-element arrangements which may include any
combination of hardware and/or service or software and T-Support. These multiple-element arrangements are
assessed to determine whether they can be separated into more than one unit of accounting or element for
the purpose of revenue recognition. When the appropriate criteria for separating revenue into more than one
unit of accounting is met and there is vendor specific objective evidence of fair value for all units of
accounting or elements in an arrangement, the arrangement consideration is allocated to the separate units of
accounting or elements based on each unit’s relative fair value. When the fair value of a delivered element has
not been established, the Company uses the residual method to recognize revenue if the fair value of
undelivered elements is determinable. This vendor specific objective evidence of fair value is established
through prices charged for each revenue element when that element is sold separately. The revenue
recognition policies described above are then applied to each unit of accounting.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and Bad Debt Expense
The Company is dependent on a number of significant customers and on large complex contracts with respect
to sales of the majority of its products, software and services. The Company expects increasing accounts
receivable balances with its large customers to continue as it sells an increasing number of its wireless devices
and software products and service relay access through network carriers and resellers rather than directly.
The Company evaluates the collectability of its accounts receivables based upon a combination of factors on
a periodic basis, such as specific credit risk of its customers, historical trends and economic circumstances.
The Company, in the normal course of business, monitors the financial condition of its customers and reviews
the credit history of each new customer. When the Company becomes aware of a specific customer’s inability
to meet its financial obligations to the Company (such as in the case of bankruptcy filings or material
deterioration in the customer’s operating results or financial position, and payment experiences), RIM records
a specific bad debt provision to reduce the customer’s related accounts receivable to its estimated net
MD&A
8