Johnson Controls 2010 Annual Report Download - page 76
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 76 of the 2010 Johnson Controls annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.76
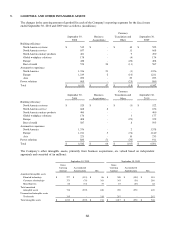
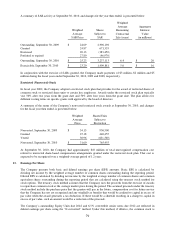
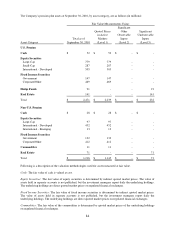
Valuation Methods
Foreign currency exchange derivatives – The Company selectively hedges anticipated transactions that are subject to
foreign exchange rate risk primarily using foreign currency exchange hedge contracts. The foreign currency
exchange derivatives are valued under a market approach using publicized spot and forward prices. As cash flow
hedges, the effective portion of the hedge gains or losses due to changes in fair value are initially recorded as a
component of accumulated other comprehensive income and are subsequently reclassified into earnings when the
hedged transactions occur and affect earnings. Any ineffective portion of the hedge is reflected in the consolidated
statement of income. These contracts are highly effective in hedging the variability in future cash flows attributable
to changes in currency exchange rates at September 30, 2010 and 2009. The fair value of foreign currency exchange
derivatives not designated as hedging instruments under ASC 815 are recorded in the consolidated statement of
income.
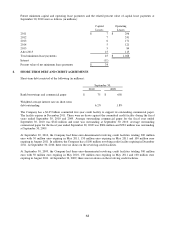
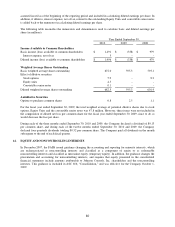
Commodity derivatives – The Company selectively hedges anticipated transactions that are subject to commodity
price risk, primarily using commodity hedge contracts, to minimize overall price risk associated with the Company’s
purchases of lead, copper and aluminum. The commodity derivatives are valued under a market approach using
publicized prices, where available, or dealer quotes. As cash flow hedges, the effective portion of the hedge gains or
losses due to changes in fair value are initially recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive
income and are subsequently reclassified into earnings when the hedged transactions, typically sales or cost related
to sales, occur and affect earnings. Any ineffective portion of the hedge is reflected in the consolidated statement of
income. These contracts are highly effective in hedging the variability in future cash flows attributable to changes in
commodity price changes at September 30, 2010 and 2009.
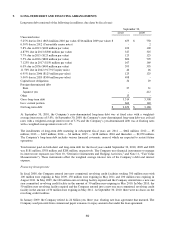
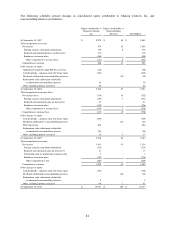
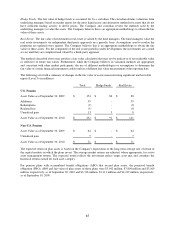
Interest rate swaps and related debt – The Company selectively uses interest rate swaps to reduce market risk
associated with changes in interest rates for its fixed-rate bonds. As fair value hedges, the interest rate swaps and
related debt balances are valued under a market approach using publicized swap curves. Changes in the fair value of
the swap and hedged portion of the debt are recorded in the consolidated statement of income. In the fourth quarter
of fiscal 2009, the Company entered into three fixed to floating interest rate swaps totaling $700 million to hedge the
coupons of its 5.25% bonds maturing on January 15, 2011. In the second quarter of fiscal 2010, the Company
terminated a $100 million portion of one of the three interest swaps mentioned above. During the second quarter of
fiscal 2010, the Company entered into a fixed to floating interest rate swap totaling $100 million to hedge the
coupons of its 5.80% bond maturing November 15, 2012 and two fixed to floating interest rate swaps totaling $300
million to hedge the coupons of its 4.875% bond maturing September 15, 2013. In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010,
the Company terminated all of its interest rate swaps. The fair value adjustments to the related debt will be
amortized over the remaining term of the debt.
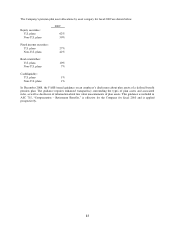
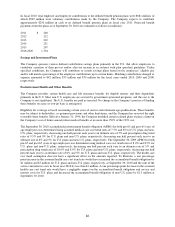
Investments in marketable common stock – The Company invested in certain marketable common stock during the
third quarter of fiscal 2010. The securities are valued under a market approach using publicized share prices. As of
September 30, 2010, the Company recorded an unrealized gain of $3 million in accumulated other comprehensive
income and no unrealized losses on these investments.
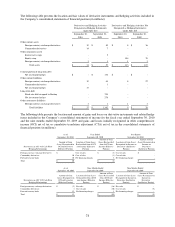
Equity swaps – The Company selectively uses equity swaps to reduce market risk associated with certain of its
stock-based compensation plans, such as its deferred compensation plans. The equity swaps are valued under a
market approach as the fair value of the swaps is based on the Company’s stock price at the reporting period date.
Changes in fair value on the equity swaps are reflected in the consolidated statement of income within selling,
general and administrative expenses.
Cross-currency interest rate swaps – The Company selectively uses cross-currency interest rate swaps to hedge the
foreign currency rate risk associated with certain of its investments in Japan. The cross-currency interest rate swaps
are valued using market assumptions. Changes in the market value of the swaps are reflected in the foreign currency
translation adjustments component of accumulated other comprehensive income where they offset gains and losses
recorded on the Company’s net investment in Japan. The Company entered into three cross-currency swaps totaling
20 billion yen during the second quarter of fiscal 2010. In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2010, a 5 billion yen cross-
currency swap expired and the Company replaced it with a new 5 billion yen cross-currency swap. These swaps are
designated as hedges in the Company’s net investment in Japan. There were no cross-currency interest rate swaps
outstanding at September 30, 2009.
Foreign currency denominated debt – The Company has entered into certain foreign currency denominated debt
obligations to selectively hedge portions of its net investment in Japan. The currency effects of the debt obligations
are reflected in the foreign currency translation adjustments component of accumulated other comprehensive income