HSBC 2001 Annual Report Download - page 269
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 269 of the 2001 HSBC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284
 |
 |

267
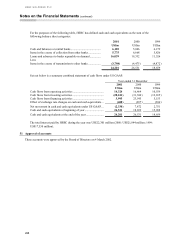
(l) Earnings per share
Basic earnings per share under US GAAP, SFAS 128 ‘Earnings per share’ , is calculated by dividing net income
of US$4,911 million (2000: US$6,236 million; 1999: US$4,889 million) by the weighted average number of
ordinary shares in issue in 2001 of 9,237 million (2000: 8,777 million; 1999: 8,296 million).
Diluted earnings per share under US GAAP is calculated by dividing net income, which requires no adjustment
for the effects of dilutive ordinary potential shares, by the weighted average number of shares outstanding plus
the weighted average number of ordinary shares that would be issued on conversion of all the dilutive potential
ordinary shares in 2001 of 9,336 million (2000: 8,865 million; 1999: 8,374 million), as shown in Note 11.
(m) Consolidated cash flow statement
HSBC prepares its cash flow statement in accordance with the UK Financial Reporting Standard 1 (Revised
1996) ‘Cash flow statements’ . Its objectives and principles are similar to those set out in SFAS 95 ‘Statement of
cash flows’ , as amended by SFAS 104 ‘Statement of cash flows – Net reporting of certain cash receipts and cash
payments and classification of cash flows from hedging transactions’ .
FRS 1 (Revised) defines cash as cash and balances at central banks and advances to banks payable on demand.
Under US GAAP, Cash equivalents are defined as short-term highly liquid investments that are both:
− convertible to known amounts of cash; and
− so near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value because of fluctuations in
interest rates.
The other principal differences between US and UK GAAP are in respect of classification. Under UK GAAP,
HSBC presents its cash flows by: (a) Operating activities; (b) Dividends received from associates; (c) Returns
on investments and servicing of finance; (d) Taxation; (e) Capital expenditure and financial investments; (f)
Acquisitions and disposals; (g) Equity dividends paid; and (h) Financing. Under US GAAP, only three
categories are required. These are: (a) Operating; (b) Investing; and (c) Financing.
Classification Under Classification Under
Cash Flow FRS 1 (Revised) SFAS 95/104
Taxation Taxation Operating activities
Dividends received from associates Dividends received from associates Operating activities
Equity dividends paid Equity dividends paid Financing activities
Non-equity dividends paid and dividends
to minority interests
Returns on investments and servicing of
finance
Financing activities
Capital expenditure and financial
investments
Capital expenditure and financial
investments
Investing activities
Transfers of subsidiary undertakings,
joint ventures and associates
Acquisitions and disposals Investing activities
Net changes in loans and advances
including finance lease payables
Operating activities Investing activities
Net changes in deposits Operating activities Financing activities
Under FRS 1 (Revised), hedges are reported under the same heading as the related assets or liabilities.
