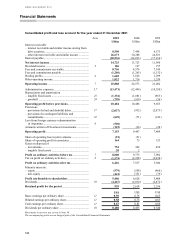
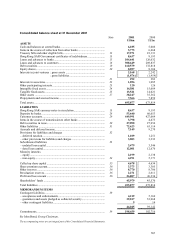
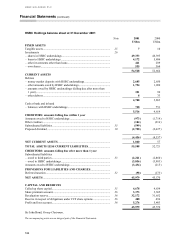
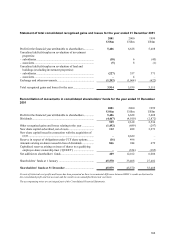
HSBC 2001 Annual Report Download - page 167
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 167 of the 2001 HSBC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
HSBC HOLDINGS PLC
Notes on the Financial Statements
165
1 Basis of preparation
(a) The financial statements have been prepared under the historical cost convention, as modified by the revaluation
of certain investments and land and buildings, and in accordance with applicable accounting standards.
The consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with the special provisions of Part VII Chapter
II of the UK Companies Act 1985 (‘the Act’ ) relating to banking groups. The consolidated financial statements
comply with Schedule 9 and the financial statements of HSBC Holdings comply with Schedule 4 to the Act.
As permitted by Section 230 of the Act, no profit and loss account is presented for HSBC Holdings.
HSBC has adopted the provisions of the UK Financial Reporting Standard (‘FRS’ ) FRS 18 ‘Accounting
Policies’ , and the transitional arrangements of FRS 17 ‘Retirement benefits’ , which require additional
disclosures only. The accounts have been prepared in accordance with the Statements of Recommended
Accounting Practice (‘SORPs’ ) issued by the British Bankers’ Association (‘BBA’ ) and Irish Bankers’
Federation (‘IBF’ ) and with the SORP ‘Accounting issues in the asset finance and leasing industry’ issued by
the Finance & Leasing Association (‘FLA’ ).
The SORP issued by the Association of British Insurers (‘ABI’ ) ‘Accounting for insurance business’ does not
address the present valuation of internally generated long-term assurance business. HSBC is primarily a banking
group, rather than an insurance group, and, consistent with other banking groups preparing consolidated
financial statements complying with Schedule 9 to the Act, values its long-term assurance businesses using the
Embedded Value method. This method includes a prudent valuation of the discounted future earnings expected
to emerge from business currently in force, taking into account factors such as recent experience and general
economic conditions, together with the surplus retained in the long-term assurance funds.
(b) The preparation of financial information requires the use of estimates and assumptions about future conditions.
This is particularly so in the development of provisions for bad and doubtful debts. Making reliable estimates of
the ability of customers and other counterparties to repay is often difficult even in periods of economic stability
and becomes more difficult in periods of economic volatility such as exists in several of HSBC’ s markets.
Therefore, while management believes it has employed all available information to estimate adequate
allowances for all identifiable risks in the current portfolios, there can be no assurance that the provisions for
bad and doubtful debts or other provisions will prove adequate for all losses ultimately realised.
(c) The consolidated financial statements of HSBC comprise the financial statements of HSBC Holdings and its
subsidiary undertakings. Financial statements of subsidiary undertakings are made up to 31 December. In the
case of the principal banking and insurance subsidiaries of HSBC Bank Argentina, whose financial statements
are made up to 30 June annually to comply with local regulations, HSBC uses audited interim financial
statements, drawn up to 31 December annually. The consolidated financial statements include the attributable
share of the results and reserves of joint ventures and associates, based on financial statements made up to dates
not earlier than six months prior to 31 December.
All significant intra-HSBC transactions are eliminated on consolidation.
(d) HSBC’ s financial statements are prepared in accordance with UK generally accepted accounting principles
(‘UK GAAP’ ), which differ in certain respects from US generally accepted accounting principles (‘US GAAP’ ).
For a discussion of significant differences between UK GAAP and US GAAP and a reconciliation to US GAAP
of certain amounts see Note 50. In addition, certain disclosures in the Notes on the Financial Statements have
been made to comply with US reporting requirements.
2 Principal accounting policies
(a) Income recognition
Interest income is recognised in the profit and loss account as it accrues, except in the case of doubtful debts
(Note 2 (b)).
Fee and commission income is accounted for in the period when receivable, except where it is charged to cover