HSBC 2001 Annual Report Download - page 172
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 172 of the 2001 HSBC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
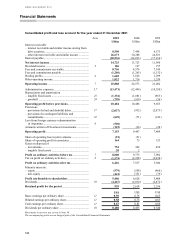
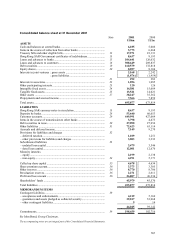
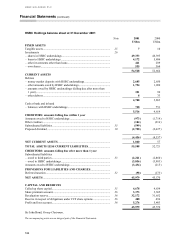
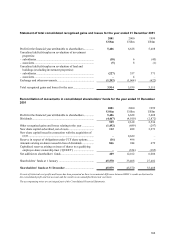
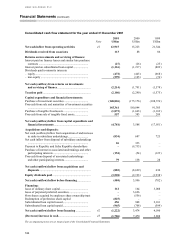
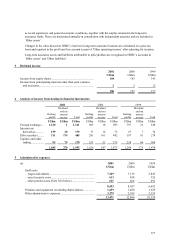
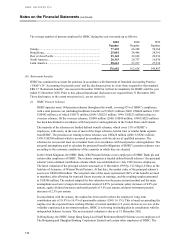
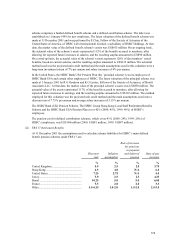
HSBC HOLDINGS PLC
Notes on the Financial Statements (continued)
170
exists. Mark-to-market assets and liabilities are presented gross, with netting shown separately.
Accounting for these instruments is dependent upon whether the transactions are undertaken for trading or non-
trading purposes.
Trading transactions
Trading transactions include transactions undertaken for market-making, to service customers’ needs and for
proprietary purposes, as well as any related hedges.
Transactions undertaken for trading purposes are marked-to-market value and the net present value of any gain
or loss arising is recognised in the profit and loss account as ‘Dealing profits’ , after appropriate deferrals for
unearned credit margin and future servicing costs. Off-balance-sheet trading transactions are valued by
reference to an independent liquid price where this is available. For those transactions where there are no readily
quoted prices, which predominantly relates to over the counter transactions, market values are determined by
reference to independently sourced rates, using valuation models. Adjustments are made for illiquid positions
where appropriate.
Assets, including gains, resulting from off-balance-sheet exchange rate, interest rate and equities contracts
which are marked-to-market are included in ‘Other assets’ . Liabilities, including losses, resulting from such
contracts, are included in ‘Other liabilities’ .
Non-trading transactions
Non-trading transactions are those which are held for hedging purposes as part of HSBC’ s risk management
strategy against assets, liabilities, positions or cash flows measured on an accruals basis. Non-trading
transactions include qualifying hedges and positions that synthetically alter the characteristics of specified
financial instruments.
Non-trading transactions are accounted for on an equivalent basis to the underlying assets, liabilities or net
positions. Any profit or loss arising is recognised on the same basis as that arising from the related assets,
liabilities or positions.
To qualify as a hedge, a derivative must effectively reduce the price or interest rate risk of the asset, liability or
anticipated transaction to which it is linked and be designated as a hedge at inception of the derivative contract.
Accordingly, changes in the market value of the derivative must be highly correlated with changes in the market
value of the underlying hedged item at inception of the hedge and over the life of the hedge contract. If these
criteria are met, the derivative is accounted for on the same basis as the underlying hedged item. Derivatives
used for hedging purposes include swaps, forwards and futures.
Interest rate swaps are also used to alter synthetically the interest rate characteristics of financial instruments. In
order to qualify for synthetic alteration, a derivative instrument must be linked to specific individual, or pools of
similar, assets or liabilities by the notional principal and interest rate risks of the associated instruments, and
must achieve a result that is consistent with defined risk management objectives. If these criteria are met,
accruals based accounting is applied, i.e. income or expense is recognised and accrued to the next settlement
date in accordance with the contractual terms of the agreement.
Any gain or loss arising on the termination of a qualifying derivative is deferred and amortised to earnings over
the original life of the terminated contract. Where the underlying asset, liability or position is sold or terminated,
the qualifying derivative is immediately marked-to-market through the profit and loss account.
Derivatives that do not qualify as hedges or synthetic alterations at inception are marked-to-market through the
profit and loss account, with gains and losses included within ‘Dealing profits’ .
(k) Long-term assurance business
The value placed on HSBC’ s interest in long-term assurance business includes a prudent valuation of the
discounted future earnings expected to emerge from business currently in force, taking into account factors such