Sears 2010 Annual Report Download - page 67
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 67 of the 2010 Sears annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SEARS HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
We record the earnings impact of mark-to-market and settlement adjustments for foreign currency collar
contracts in other income (loss) at the end of each period. We recorded mark-to-market and settlement losses on
these contracts of $14 million and $77 million in other income (loss) for years ended January 29, 2011 and
January 30, 2010, respectively.
Sears Canada’s above noted foreign currency collar contracts were entered into as a hedge of merchandise
purchase contracts denominated in U.S. currency. We also record mark-to-market adjustments for the value of
the merchandise purchase contracts (considered to be embedded derivatives under relevant accounting rules) at
the end of each period. We recorded an asset of $2 million at January 29, 2011 related to the fair value of these
embedded derivatives. These embedded derivates had a zero fair value at January 30, 2010.
We record the earnings impact of mark-to-market and settlement adjustments related to the embedded
derivative in the merchandise purchase contracts in other income (loss) at the end of each period. We recorded
mark-to-market and a settlement loss of $1 million for the year ended January 29, 2011 and mark-to-market and
settlement gains of $10 million for the year ended January 30, 2010.
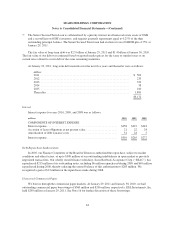
At January 29, 2011, we had total derivative mark-to-market liabilities related to the collar contracts and
embedded derivatives of $1 million. We recorded total mark-to-market losses and settlements of $15 million in
other income (loss) for the year ending January 29, 2011. At January 30, 2010, we had total derivative
mark-to-market assets related to the collar contracts and embedded derivatives of $9 million. We recorded total
mark-to-market losses and settlements of $67 million in other income (loss) for the year ending January 30,
2010. See Note 5 for further information regarding fair value of these collar and merchandise purchase contracts
and the respective balance sheet classifications at January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010.
Hedges of Net Investment in Sears Canada
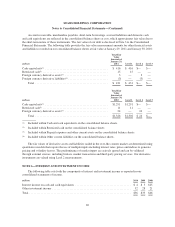
At January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, we had a series of foreign currency forward contracts
outstanding with a total Canadian notional value of $629 million and $400 million, respectively, and with a
weighted-average remaining life of 0.5 years. These contracts were designated and qualified as hedges of the
foreign currency exposure of our net investment in Sears Canada. Accordingly, the aggregate fair value of the
forward contracts at January 29, 2011 and January 30, 2010, of approximately $1 million and $15 million,
respectively, was recorded as an asset on our consolidated balance sheet. The decline in fair value of $14 million
related to these forward contracts, net of tax, was recorded as a component of other comprehensive income for
the 52-week period ended January 29, 2011.
We settled certain foreign currency forward contracts during 2010 and paid a net amount of $3 million
relative to these contract settlements. During fiscal 2008, we paid a net amount of $64 million to settle certain
foreign currency forward contracts entered into in prior years. As hedge accounting was applied to such
contracts, an offsetting amount was recorded as a component of other comprehensive income.
Certain of our currency forward contracts require collateral be posted in an amount equal to the liability
under such contracts. Cash collateral posted under these contracts is recorded as part of our accounts receivable
balance. We had $3 million of cash collateral posted under these contracts at January 29, 2011. We did not have
any cash collateral posted under these contracts as of January 30, 2010. We had no such foreign currency forward
contracts outstanding as of January 31, 2009.
Counterparty Credit Risk
We actively manage the risk of nonpayment by our derivative counterparties by limiting our exposure to
individual counterparties based on credit ratings, value at risk and maturities. The counterparties to these
instruments are major financial institutions with credit ratings of single-A or better at January 29, 2011.
67