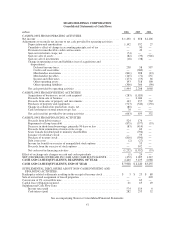
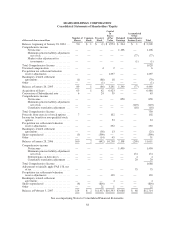
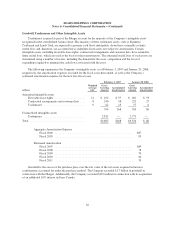
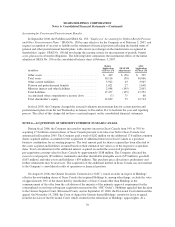
Sears 2006 Annual Report Download - page 64
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 64 of the 2006 Sears annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SEARS HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
income in the same account as the hedged item, as a component of interest expense. Changes in the fair value of
interest rate swaps and caps that do not qualify as hedges are recognized currently as a component of interest
expense. The foreign currency forward contracts are recorded on the consolidated balance sheet at fair value and,
to the extent they have been designated and qualify for hedge accounting treatment, an offsetting amount is
recorded as a component of other comprehensive income. Changes in the fair value of those forward contracts for
which hedge accounting is not applied are recorded in the consolidated statement of income as a component of
other income.
The Company has total return swaps as a means for investing a portion of the Company’s surplus cash.
Changes in the fair value of the total return swaps are recognized as a component of interest and investment
income in the Company’s consolidated statements of income as they occur.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, merchandise payables, credit facility borrowings and
accrued liabilities are reflected in the consolidated balance sheet at cost, which approximates fair value due to the
short-term nature of these instruments. The fair value of the Company’s debt and derivative financial instruments
are disclosed in Note 7 and Note 8, respectively.
Financial instruments that potentially subject Holdings to concentration of credit risk consist principally of
temporary cash investments, accounts receivable and derivative financial instruments. The Company places its
cash and cash equivalents in investment-grade, short-term instruments with high quality financial institutions
and, by policy, limits the amount of credit exposure in any one financial instrument. The Company uses high
credit quality counterparties to transact its derivative transactions.
Self-insurance Reserves
The Company is self-insured for certain costs related to health, workers’ compensation, asbestos and
environmental, automobile, warranty, product and general liability claims. The Company obtains third-party
insurance coverage to limit its exposure to certain of these self-insured risks. A portion of these self-insured risks
is managed through a wholly-owned insurance subsidiary. The Company’s liability reflected on the consolidated
balance sheet, classified within other liabilities (current and long-term), represents an estimate of the ultimate
cost of claims incurred as of the balance sheet date. In estimating this liability, the Company utilizes loss
development factors based on Company-specific data to project the future development of incurred losses. Loss
estimates are adjusted based upon actual claims settlements and reported claims. The liabilities for self-insured
risks are discounted to their net present values.
Loss Contingencies
The Company accounts for contingent losses in accordance with SFAS No. 5, “Accounting for
Contingencies.” Under SFAS No. 5, loss contingency provisions are recorded for probable losses at
management’s best estimate of a loss, or when a best estimate cannot be made, a minimum loss contingency
amount is recorded. These estimates are often initially developed substantially earlier than the ultimate loss is
known, and the estimates are refined each accounting period, as additional information is known.
Revenue Recognition
Revenues include sales of merchandise, services and extended service contracts, net commissions earned
from leased departments in retail stores, delivery and handling revenues related to merchandise sold, and fees
64