Kodak 2003 Annual Report Download - page 52
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 52 of the 2003 Kodak annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Financials
52
The aggregate amount of intangible assets acquired during 2003 of
$204 million was attributable to $169 million for the purchase of
PracticeWorks as described in Note 21, “Acquisitions,” and $35 million
related to additional acquisitions that are all individually immaterial. The
aggregate amount of intangible assets acquired during 2002 of $15 mil-
lion was attributable to acquisitions that were all individually immaterial.
Amortization expense related to intangible assets was $28 million,
$21 million and $15 million in 2003, 2002 and 2001, respectively.
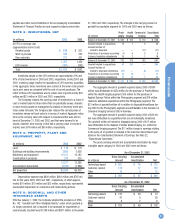
Estimated future amortization expense related to purchased intangi-
ble assets at December 31, 2003 is as follows:
(in millions)
2004 $ 42
2005 40
2006 34
2007 30
2008 26
2009+ 122
Total $ 294
NOTE 6: OTHER LONG-TERM ASSETS
(in millions) 2003 2002
Prepaid pension costs $ 1,147 $ 988
Investments in unconsolidated affiliates 426 382
Deferred income taxes 378 421
Intangible assets other than goodwill 294 118
Non-current receivables 254 328
Miscellaneous other long-term assets 386 322
Total $ 2,885 $ 2,559
The miscellaneous component above consists of other miscellaneous
long-term assets that, individually, are less than 5% of the Company’s
total long-term assets, and therefore, have been aggregated in accor-
dance with Regulation S-X.
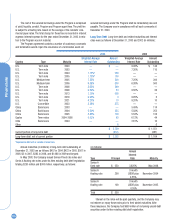
NOTE 7: INVESTMENTS
Equity Method At December 31, 2003, the Company’s significant equity
method investees and the Company’s approximate ownership interest in
each investee were as follows:
Kodak Polychrome Graphics (KPG) 50%
Express Stop Financing (ESF) 50%
NexPress Solutions LLC 50%
SK Display Corporation 34%
Matsushita-Ultra Technologies Battery Corporation 30%
At December 31, 2003 and 2002, the Company’s equity investment
in these unconsolidated affiliates was $417 million and $381 million,
respectively, and is reported within other long-term assets in the accom-
panying Consolidated Statement of Financial Position. The Company
records its equity in the income or losses of these investees and reports
such amounts in other charges, net, in the accompanying Consolidated
Statement of Earnings. See Note 14, “Other Charges, Net.” These invest-
ments do not meet the Regulation S-X significance test requiring the
inclusion of the separate investee financial statements.
The Company sells graphics film and other products to its equity
affiliate, KPG. Sales to KPG for the years ended December 31, 2003, 2002
and 2001 amounted to $271 million, $315 million and $350 million,
respectively. These sales are reported in the Consolidated Statement of
Earnings. The Company eliminates profits on these sales, to the extent the
inventory has not been sold through to third parties, on the basis of its
50% interest. At December 31, 2003 and 2002, amounts due from KPG
relating to these sales were $6 million and $31 million, respectively, and
are reported in receivables, net in the accompanying Consolidated
Statement of Financial Position. Additionally, the Company has guaranteed
certain debt obligations of KPG up to $160 million, which is included in the
total guarantees amount of $363 million at December 31, 2003, as dis-
cussed in Note 12, “Guarantees.”
Kodak sells certain of its long-term lease receivables relating to the
sale of photofinishing equipment to ESF without recourse to the Company.
Sales of long-term lease receivables to ESF were approximately $15 mil-
lion, $9 million and $83 million in 2003, 2002 and 2001, respectively. See
Note 11, “Commitments and Contingencies.”
As disclosed in Note 1, the provisions of FIN 46 were applied to ESF
for the year ended December 31, 2003 because ESF qualifies as a vari-
able interest entity (VIE) and meets the definition of a special purpose enti-
ty as defined in FIN 46. The Company’s wholly owned subsidiary, Qualex,
is not the primary beneficiary of ESF as determined in accordance with
FIN 46 and, therefore, is not required to consolidate ESF. ESF is an operat-
ing entity formed between Qualex and Dana Credit Corporation in October
1993 to provide a long-term financing solution to Qualex’s photofinishing
customers in connection with Qualex’s leasing of photofinishing equipment
to third parties, as opposed to Qualex extending long-term credit (see Note
11 under “Other Commitments and Contingencies”). Qualex’s estimated
maximum exposure to loss as a result of its continuing involvement with
ESF is $51 million as of December 31, 2003, which is equal to the carry-
ing value of Qualex’s investment balance in the entity. As of December 31,
2003, the Company does not intend to nor is committed to fund any
amounts to ESF in the future, and there are no debt guarantees under
which Qualex could potentially be required to perform in relation to its
investment in ESF. The Company was not involved with any other entities
which would qualify as VIEs under the Revised Interpretations of FIN 46.
The Company also sells chemical products to its 50% owned equity
affiliate, NexPress. These sales transactions are not material to the
Company’s financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
On March 8, 2004, the Company announced that it had agreed with
Heidelberger Druckmaschinen AG (Heidelberg) to purchase Heidelberg’s 50
percent interest in NexPress. Refer to Note 25, “Subsequent Events,” for
further discussion of this purchase.
Kodak has no other material activities with its equity method
investees.
Cost Method The Company also has certain investments with less than a
20% ownership interest in various private companies whereby the
Company does not have the ability to exercise significant influence. These
investments are accounted for under the cost method. The remaining car-
rying value of the Company’s investments accounted for under the cost
method at December 31, 2003 and 2002 of $25 million and $29 million,