Cigna 2008 Annual Report Download - page 136
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 136 of the 2008 Cigna annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
116
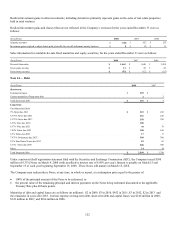
Actual maturities could differ from contractual maturities because issuers may have the right to call or prepay obligations, with or
without penalties. Also, in some cases the Company may extend maturity dates.
Mortgage-backed assets consist principally of commercial mortgage-backed securities and collateralized mortgage obligations of which
$41 million were residential mortgages and home equity lines of credit, all of which were originated utilizing standard underwriting
practices and are not considered sub-prime loans.
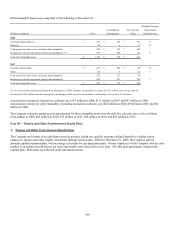
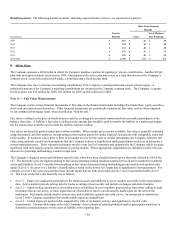
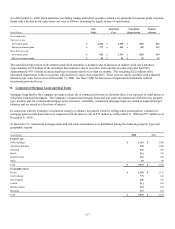
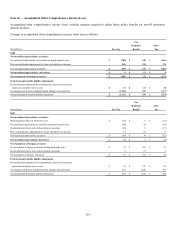
Gross unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on fixed maturities (excluding trading securities and hybrid securities) by type of issuer is
shown below.
December 31, 2008
Unrealized Unrealized
Amortized Appre- Depre- Fair
(In millions) Cost ciation ciation Value
Federal government and agency $ 359 $ 403 $ - $ 762
State and local government 2,391 117 (22) 2,486
Foreign government 882 70 (8) 944
Corporate 7,197 167 (529) 6,835
Federal agency mortgage-backed (1) 36 1 - 37
Other mortgage-backed 149 - (25) 124
Other asset-backed 455 128 (13) 570
Total $ 11,469 $ 886 $ (597) $ 11,758
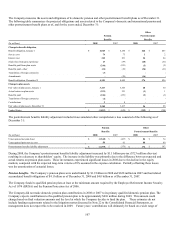
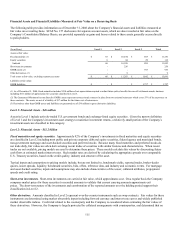
(In millions) December 31, 2007
Federal government and agency $ 346 $ 282 $ - $ 628
State and local government 2,362 130 (3) 2,489
Foreign government 868 32 (18) 882
Corporate 7,157 318 (85) 7,390
Other mortgage-backed 216 6 (2) 220
Other asset-backed 427 29 (17) 439
Total $ 11,376 $ 797 $ (125) $ 12,048
(1) Federal agency mortgage-backed securities were first purchased in 2008 as part of the acquired business.
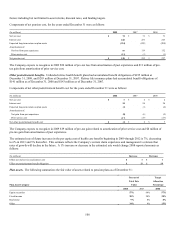
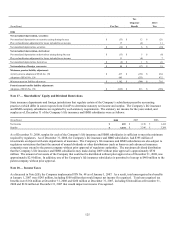
The above table includes investments with a fair value of $2.5 billion supporting the Company’s run-off settlement annuity business,
with gross unrealized appreciation of $624 million and gross unrealized depreciation of $110 million at December 31, 2008. Such
unrealized amounts are required to support future policy benefit liabilities of this business and, accordingly, are not included in
accumulated other comprehensive income. At December 31, 2007, investments supporting this business had a fair value of $2.6
billion, gross unrealized appreciation of $476 million and gross unrealized depreciation of $20 million.
As of December 31, 2008, the Company had no outstanding commitments to purchase fixed maturities.
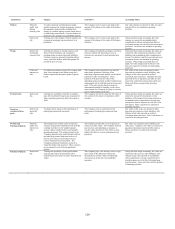
Review of declines in fair value. Management reviews fixed maturities and equity securities for impairment based on criteria that
include:
• length of time and severity of decline;
• financial health and specific near term prospects of the issuer;
• changes in the regulatory, economic or general market environment of the issuer’s industry or geographic region; and
• the Company’s ability and intent to hold until recovery.