Berkshire Hathaway 2001 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
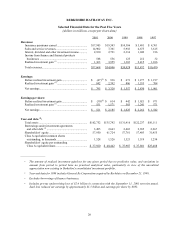
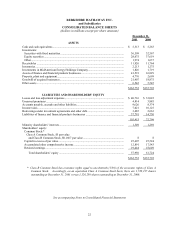
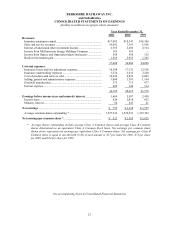
Please find page 28 of the 2001 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.27
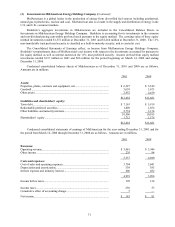
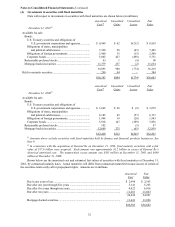
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices (Continued)
(e) Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. Cost with respect to manufactured goods includes raw
materials, direct and indirect labor and factory overhead. Approximately 46% of the total inventory cost
was determined using the first-in-first-out (FIFO) method with the remainder valued using the last-in-
first-out (LIFO) method. With respect to inventories carried at LIFO cost, the aggregate difference in
value between LIFO cost and cost determined under FIFO methods was not material as of December 31,
2001 and December 31, 2000.
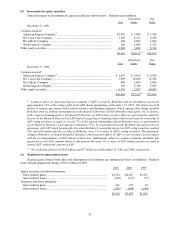
(f) Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment is recorded at cost. Depreciation is provided principally on the straight-line
method over estimated useful lives as follows: aircraft, simulators, training equipment and spare parts, 4
to 20 years; buildings and improvements, 10 to 40 years; machinery, equipment, furniture and fixtures, 3
to 20 years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the life of the lease or the life of the
improvement, whichever is shorter. Interest is capitalized as an integral component of cost during the
construction period of simulators and facilities and is amortized over the life of the related assets.
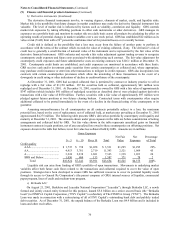
(g) Goodwill of acquired businesses
Goodwill of acquired businesses represents the difference between purchase cost and the fair value of the
net assets of acquired businesses and is being amortized on a straight-line basis generally over 40 years.
The Company periodically reviews the recoverability of the carrying value of goodwill of acquired
businesses to ensure it is appropriately valued. In the event that a condition is identified which may
indicate an impairment issue exists, an assessment is performed using a variety of methodologies.
As a result of new accounting standards issued in June 2001, accounting for goodwill has changed.
Goodwill arising from business acquisitions after July 1, 2001 is subject to an impairment only model,
instead of an amortization and impairment model. See Note 1(n) below for further discussion of these
new standards.
During the fourth quarter of 2000, Berkshire management concluded that an impairment of goodwill
existed with respect to the Dexter Shoe business. Goodwill amortization shown in the accompanying
Consolidated Statements of Earnings for 2000 includes a goodwill impairment charge of $219 million
related to this business.
(h) Revenue recognition
Insurance premiums for prospective property/casualty insurance and reinsurance and health reinsurance
policies are earned in proportion to the level of insurance protection provided. In most cases, premiums
are recognized as revenues ratably over their terms with unearned premiums computed on a monthly or
daily pro rata basis. Premium adjustments on contracts and audit premiums are based on estimates made
over the contract period. Consideration received for retroactive reinsurance policies is recognized as
premiums earned at the inception of the contracts. Premiums for life contracts are earned when due.
Premiums earned are stated net of amounts ceded to reinsurers.
Revenues from product sales are recognized upon passage of title to the customer, which coincides with
customer pickup, product shipment, delivery or acceptance, depending on terms of the sales arrangement.
Service revenues are recognized as the services are performed. Services provided pursuant to a contract
are either recognized over the contract period, or upon completion of the elements specified in the
contract, depending on the terms of the contract.
(i) Insurance premium acquisition costs
Certain costs of acquiring insurance premiums are deferred, subject to ultimate recoverability, and charged
to income as the premiums are earned. Acquisition costs consist of commissions, premium taxes,
advertising and other underwriting costs. The recoverability of premium acquisition costs, generally,
reflects anticipation of investment income. The unamortized balances of deferred premium acquisition
costs are included in other assets and were $1,029 million and $916 million at December 31, 2001 and
2000, respectively.